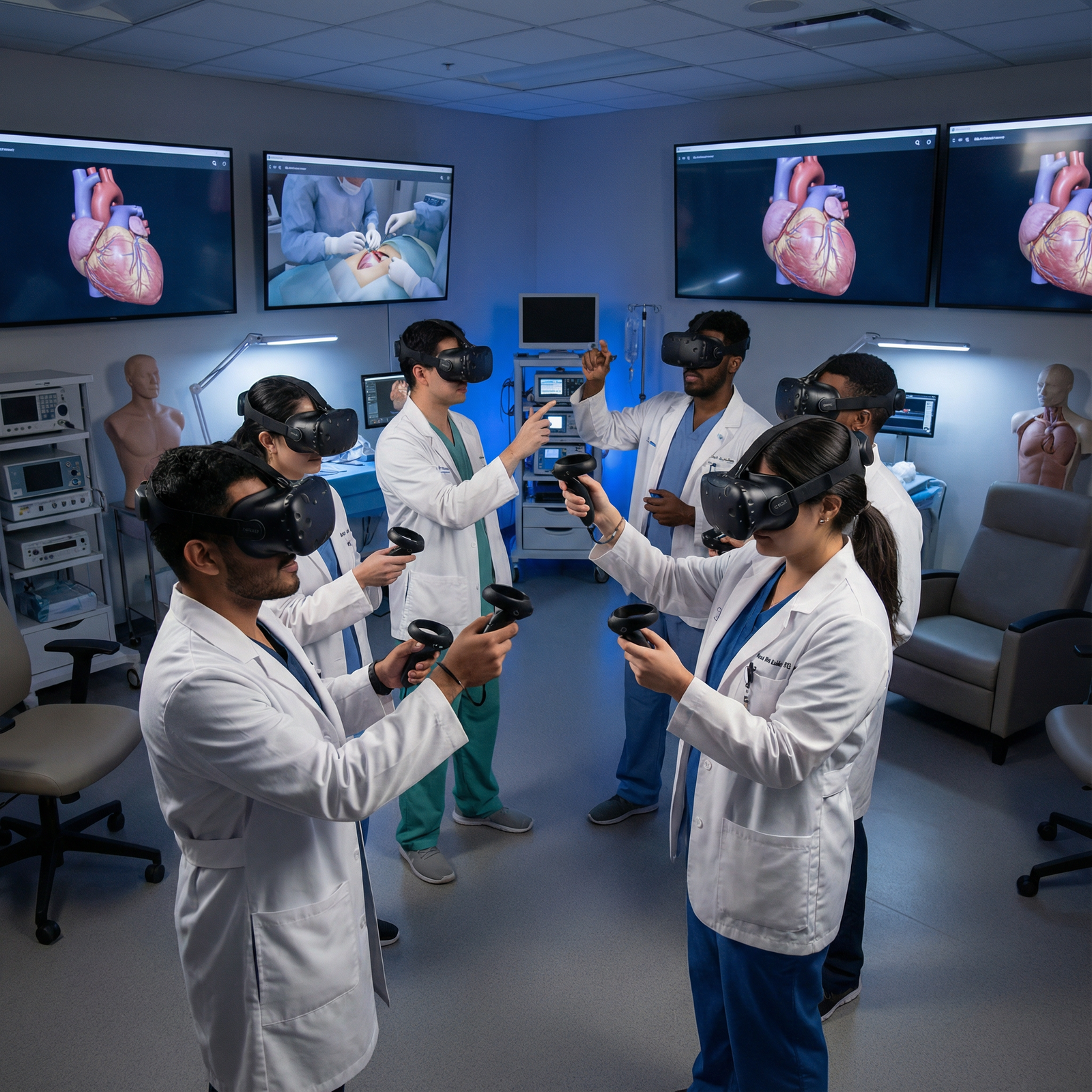
Introduction: Virtual Reality at the Heart of the Future of Healthcare
Technology in medicine is advancing at a pace that is reshaping how future physicians learn, practice, and deliver care. Among the most disruptive tools is Virtual Reality (VR)—no longer just a gaming novelty, but a powerful engine for healthcare training and medical education.
VR now allows medical students and residents to:
- Practice complex procedures repeatedly with no risk to patients
- Experience rare clinical cases they might never see during rotations
- Collaborate in virtual operating rooms and emergency departments
- Learn anatomy and clinical reasoning in deeply immersive 3D environments
As the Future of Healthcare becomes increasingly digital and data-driven, virtual reality is emerging as a core component of how we train clinicians. This article explores what VR is, where it fits in medical and residency training, its benefits and limitations, real-world case studies, and how you—as a current or future trainee—can position yourself to take advantage of this evolving landscape.
Understanding Virtual Reality in Medical Education
What Exactly Is Virtual Reality?
Virtual Reality is a computer-generated, three-dimensional environment that users can interact with using specialized hardware such as:
- VR headsets (e.g., Meta Quest, HTC Vive, Varjo, Pico)
- Hand controllers or haptic devices
- Motion tracking systems for hands, head, and sometimes full body
When you put on a VR headset, your visual and auditory inputs are replaced by a digital world. High-quality VR can create a strong sense of “presence”—the feeling that you are truly there in the virtual environment. In healthcare training, that “there” might be:
- A virtual operating room
- A busy emergency department resuscitation bay
- A primary care exam room
- A 3D interactive anatomy lab
You can reach out to “touch” organs, manipulate instruments, perform procedures, and communicate with virtual patients or teammates.
Why VR Has Gained Momentum in Medicine
Initially, VR’s progress was driven by the gaming and entertainment industry, but medicine quickly recognized its unique advantages:
- High-stakes practice with zero risk
- Standardized, repeatable scenarios for assessment
- On-demand access to training regardless of physical location
The COVID-19 pandemic dramatically accelerated adoption. Suddenly, many in-person clinical experiences and anatomy labs were disrupted. Programs had to innovate rapidly, and VR became an essential part of blended and remote learning strategies.
Key Application Areas of VR in Healthcare Training
Realistic Patient Simulations
- Encounters with standardized virtual patients who present with symptoms, emotions, and physical findings
- Practice history-taking, physical exam, shared decision-making, and delivering difficult news
- Objective tracking of communication, empathy, and diagnostic reasoning
Surgical and Procedural Practice
- Simulate laparoscopic, endoscopic, robotic, and open procedures
- Learn stepwise techniques with real-time error feedback (e.g., excessive force, incorrect angle)
- Build psychomotor skills and muscle memory before ever entering the OR
3D Anatomical Learning
- Explore layered anatomy—muscles, nerves, vasculature, organs—in full 3D
- Visualize spatial relationships that are hard to grasp from 2D atlases
- “Dissect” and reassemble structures repeatedly without specimen limitations
Interprofessional and Team-Based Training
- Physicians, nurses, pharmacists, EMS, and therapists can train together
- Practice crisis resource management, closed-loop communication, and leadership in high-acuity scenarios
- Standardized debriefing using recorded VR sessions
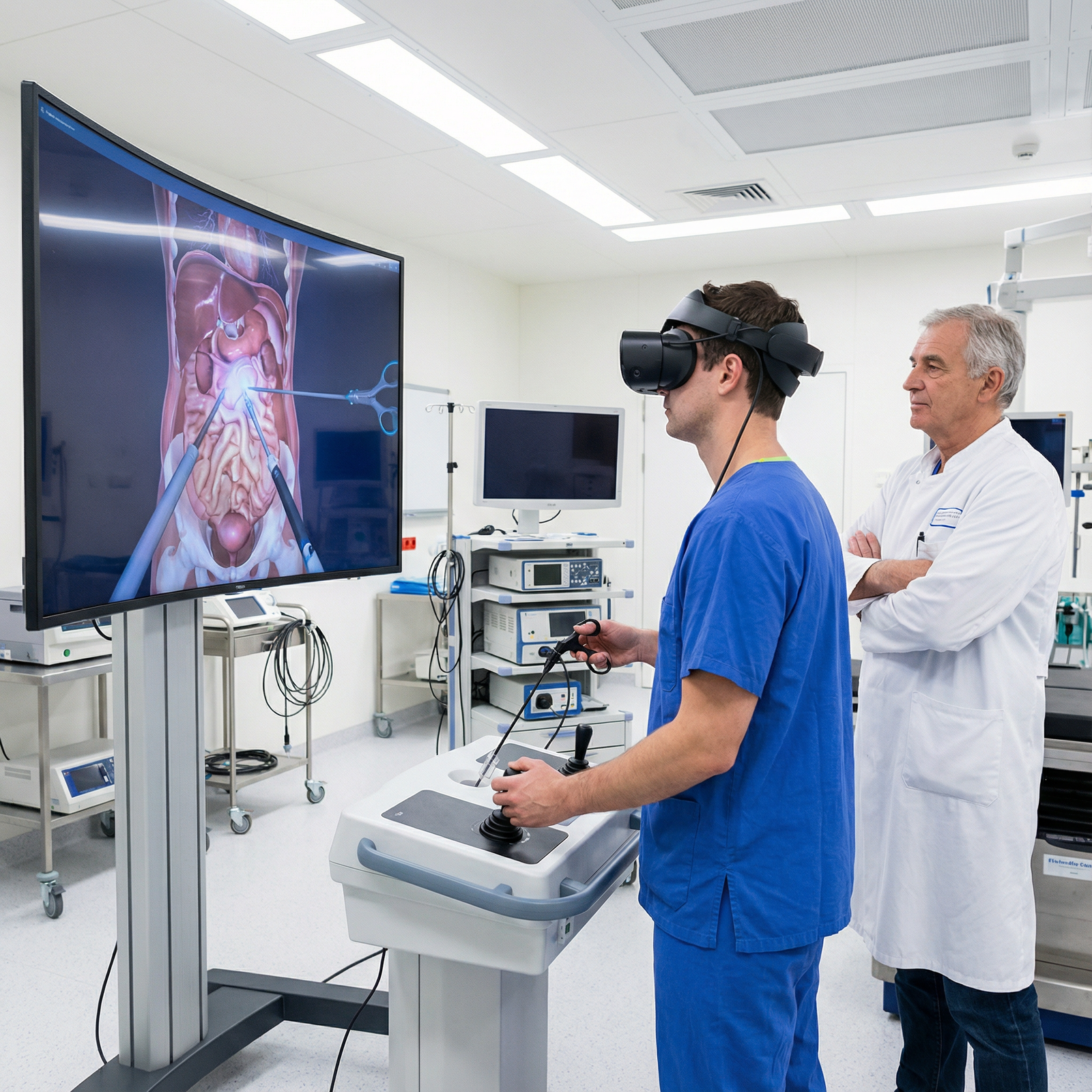
Benefits of Virtual Reality Training for Medical Students and Residents
VR offers more than novelty; it changes how information is encoded, practiced, and retained. The benefits extend across cognitive, psychomotor, and affective domains of learning.
1. Immersive, Multisensory Learning That Sticks
Traditional lectures and 2D slides are largely passive. VR, by contrast, engages:
- Visual learning: 3D spatial relationships and dynamic visualization
- Auditory learning: Heart sounds, breath sounds, alarms, team communication
- Kinesthetic learning: Hand movements with instruments, positioning, coordination
Research in technology in medicine education suggests that immersive experiences can:
- Improve knowledge retention compared with text or video alone
- Enhance procedural performance metrics (accuracy, time to completion, error rates)
- Increase learner engagement and motivation, a key predictor of long-term mastery
Example: A resident practicing a laparoscopic cholecystectomy in VR can repeatedly see and feel the correct orientation of instruments, spatial relationships of Calot’s triangle, and safe dissection planes—leading to better performance in the live OR.
2. A Safe Space to Fail, Learn, and Repeat
In real clinical settings, opportunities to “practice” are constrained by:
- Patient safety
- Limited time and supervision
- Ethical considerations
VR removes these constraints:
- You can make mistakes, analyze them, and try again—without harm.
- Rare or critical scenarios (e.g., pediatric cardiac arrest, obstetric emergencies) can be practiced repeatedly.
- Residents can rehearse upcoming procedures before they’re done on actual patients.
This safe learning environment builds:
- Confidence and readiness
- Reduced performance anxiety in real settings
- A culture where error analysis is normalized and productive
3. Accessibility, Flexibility, and Scalability
VR-based healthcare training offers:
- Geographic flexibility: Learners in remote or resource-limited settings can access high-quality simulations if they have a headset and internet.
- Time flexibility: Residents can train during off-hours, after call, or between clinics without needing a full sim lab setup.
- Scalable teaching: One carefully designed VR scenario can be used by hundreds of learners across multiple campuses or countries.
For institutions struggling with cadaver availability, faculty bandwidth, or limited simulation centers, VR can extend capacity significantly.
4. Enhanced Collaboration and Team-Based Skills
Medicine is fundamentally a team sport. VR platforms now support:
- Multiuser environments where learners “meet” inside the same virtual OR or ED
- Role assignment (e.g., team leader, airway, medications, documentation)
- Integrated audio for real-time communication and closed-loop responses
This builds essential skills for the future of healthcare, including:
- Interprofessional collaboration
- Situational awareness and leadership
- Conflict management and shared decision-making
5. Personalized, Data-Driven Learning Pathways
Unlike traditional simulations that rely heavily on human observation, VR systems automatically track granular performance data:
- Time to diagnosis or intervention
- Number and type of errors (e.g., vessel injury, incorrect medication dose)
- Adherence to clinical guidelines and checklists
- Precision and efficiency of instrument handling
These data make it possible to:
- Tailor training to each learner’s strengths and weaknesses
- Provide targeted remediation or advanced modules
- Use objective metrics for competency assessments and entrustable professional activities (EPAs)
As VR increasingly integrates with Artificial Intelligence (AI), future platforms will dynamically adapt scenario difficulty in real time based on a learner’s performance.
Challenges, Limitations, and Practical Considerations
Despite its promise, VR is not a magic bullet. Successful integration into medical education requires recognizing and addressing several key challenges.
1. Cost, Infrastructure, and Institutional Readiness
Barriers for schools and residency programs include:
- Hardware: Headsets, controllers, powerful PCs (for tethered systems), network upgrades
- Software: Licensing fees for commercial VR platforms and content
- Facilities: Space for VR labs, infection control for shared equipment
- Support: IT staff, simulation specialists, and educational designers
Strategies to manage cost:
- Start with pilot programs in high-yield domains (e.g., anatomy, basic procedural skills)
- Use standalone headsets that reduce the need for high-end PCs
- Form consortia across institutions to share costs and content
- Seek grants, philanthropic support, or industry-academic partnerships
2. Technical Skills and User Experience
Adoption can be slowed by:
- Faculty unfamiliarity with VR hardware and software
- Motion sickness or “VR fatigue” in some learners
- Poorly designed interfaces or non-intuitive controls
Mitigation strategies:
- Provide brief onboarding sessions and quick-start guides
- Involve clinician educators in content design to ensure clinical realism and usability
- Start with shorter sessions, gradually increasing duration as users acclimate
- Offer “VR champions” or super-users among residents and faculty to support peers
3. Content Gaps and Quality Control
Not all VR content is created equal. Current limitations include:
- Incomplete coverage of all specialties and procedures
- Variable realism in anatomy, pathology, and patient behavior
- Insufficient alignment with local curricula or national competency frameworks
Programs should:
- Evaluate VR offerings based on evidence, validation studies, and alignment with learning objectives
- Collaborate with vendors to co-develop content tailored to specific curricula
- Use instructional design principles (clear objectives, scaffolded complexity, feedback, debriefing) instead of treating VR as “edutainment”
4. Ethical, Professional, and Humanistic Considerations
While VR can simulate clinical reality, it also raises important questions:
- Could overexposure to virtual patients desensitize learners?
- How do we ensure that empathy, cultural humility, and professionalism are cultivated—not undermined?
- Are there privacy or data concerns with recording learner performance and behavior?
Ethical best practices:
- Use VR scenarios that explicitly emphasize empathy and patient-centered communication
- Combine VR with structured debriefs focused on reflection, emotions, and professionalism
- Ensure transparency about data collection, storage, and use for assessment
- Seek input from ethics committees and patient representatives when designing emotionally charged simulations (e.g., end-of-life care)
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
VR in healthcare training is no longer hypothetical—it is being implemented across leading institutions worldwide. Here are expanded examples plus additional contexts where VR is making a measurable difference.
Case Study 1: USC Keck School of Medicine – Next-Generation Anatomy
USC’s Keck School of Medicine incorporated VR into its anatomy curriculum:
- Students use VR applications to explore a lifelike 3D human body.
- They can isolate systems (musculoskeletal, cardiovascular, nervous) and view structures from any angle.
- Layers can be added or removed to understand anatomical relationships that are difficult to appreciate in cadaveric dissection alone.
Reported benefits:
- Improved spatial understanding and recall during exams
- Stronger correlation between anatomical knowledge and imaging interpretation
- More equitable experience—every student can visualize the same high-quality structures, regardless of variability between cadavers
Case Study 2: Stanford University – Communication and Clinical Encounters
Stanford’s programs use VR to focus not just on technical skills, but also on soft skills:
- Students enter virtual exam rooms to interview and examine simulated patients.
- Virtual patients can display realistic emotional states—anxiety, anger, sadness, confusion.
- Scenarios include common yet challenging communication tasks: breaking bad news, discussing goals of care, addressing non-adherence, or managing bias and microaggressions.
Outcomes noted:
- Enhanced confidence in patient communication
- Improved structure and clarity of clinical interviews
- Richer opportunities for feedback as faculty and peers can watch recorded VR sessions and pause to discuss alternative approaches
Case Study 3: Immersive VR Education’s "Engage" Platform – Global Collaboration
Immersive VR Education’s Engage platform is used by medical schools worldwide:
- Enables real-time collaboration among learners and instructors from different institutions and countries.
- Hosts virtual classrooms, clinical case conferences, and simulated ward rounds.
- Facilitates global health education, enabling students in low-resource settings to access world-class training environments.
Impact:
- Enhanced clinical reasoning and decision-making through interactive, case-based learning
- Exposure to diverse practice patterns and health systems
- Development of global, cross-cultural perspectives on care delivery
Additional Areas Where VR Is Transforming Training
Beyond the cases above, innovative uses of VR include:
- Emergency medicine and trauma: Multi-casualty incidents, disaster response, mass casualty triage
- Obstetrics and gynecology: Shoulder dystocia, postpartum hemorrhage, complex pelvic surgeries
- Cardiology: Interventional cardiology procedures, structural heart interventions
- Psychiatry: Exposure therapy models (primarily for patients), and training clinicians to recognize and manage psychiatric emergencies
- Primary care and telemedicine: Remote consultation simulations, chronic disease management, and motivational interviewing practices
Each of these domains demonstrates how VR is becoming a backbone of modern technology in medicine and the broader future of healthcare workforce training.
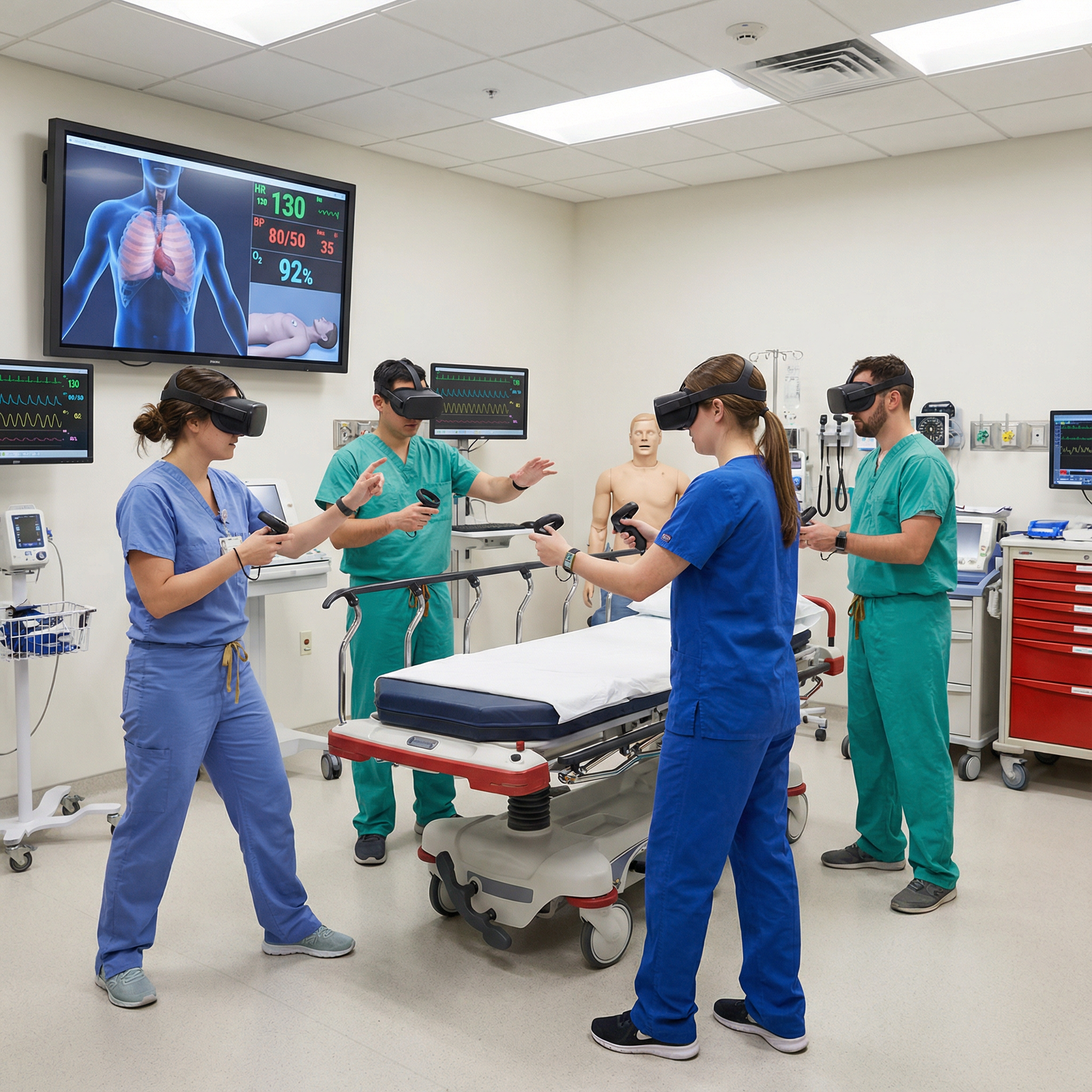
Looking Ahead: How Virtual Reality Will Shape the Future of Healthcare Training
The coming decade will likely see VR move from “innovative add-on” to standard infrastructure for medical and residency education.
1. Widespread Adoption and Integration Across Curricula
Expect to see:
- VR embedded into preclinical courses (anatomy, physiology, pathology)
- Routine use of VR for OSCE preparation, procedural checklists, and clinical reasoning cases
- Integration into maintenance of certification and continuing professional development for practicing clinicians
As more outcome data accumulate, accreditation bodies and specialty boards may recognize VR-based competencies as part of official training milestones.
2. AI-Enhanced, Adaptive VR Learning
Integration with Artificial Intelligence will allow VR platforms to:
- Analyze learner performance in real time
- Adjust difficulty, case complexity, and pacing on the fly
- Generate personalized recommendations, micro-lessons, or remediation exercises
- Simulate more nuanced, realistic patient behaviors and team dynamics
This synergy of VR and AI will push the boundaries of personalized medical education.
3. Interdisciplinary and Cross-Sector Collaboration
Future VR ecosystems will likely involve:
- Medical schools, nursing schools, pharmacy programs, allied health training, and EMS academies all sharing common scenarios
- Collaboration with engineers, game designers, and human factors specialists
- Industry partnerships to simulate new devices, implants, and surgical robots before they reach the clinical environment
This will foster a generation of clinicians who are comfortable working at the intersection of healthcare and advanced technology, a critical skill set for the future of medicine.
4. Global Access and Equity in Training
If implemented thoughtfully, VR can help reduce disparities in training:
- Remote and underserved regions can gain access to high-quality, standardized curricula.
- International partnerships can support capacity-building in low- and middle-income countries.
- Cloud-based VR platforms can disseminate best practices rapidly during emerging crises (e.g., outbreaks, new therapies, or procedures).
Ensuring equitable access will require attention to device cost, bandwidth limitations, and culturally relevant content—but the potential for global impact is significant.
Actionable Advice for Medical Students and Residents
If you are a current or aspiring physician, you can position yourself at the forefront of this transformation:
- Seek out VR opportunities at your institution: simulation centers, elective rotations, or research projects.
- Document your VR training: log hours, cases, and competencies practiced; highlight this experience in your CV and during interviews, especially for procedure-heavy specialties.
- Provide feedback to educators and vendors: your insights can help refine scenarios and prioritization of skills.
- Consider scholarly work: QI projects, educational research, or presentations on VR implementation and outcomes can strengthen your academic profile.
- Think critically: Always link VR experiences back to clinical reality—ask how what you practiced translates to patient care and real-world constraints.
FAQs: Virtual Reality in Medical Education and Healthcare Training
1. Is virtual reality meant to replace traditional medical training?
No. VR is a complement, not a replacement. Cadaver dissection, bedside teaching, operating room experience, and real patient interactions remain indispensable. VR enhances these experiences by:
- Allowing safe, repeated practice before live encounters
- Standardizing exposure to rare or high-risk scenarios
- Providing data-driven feedback that is hard to obtain in busy clinical environments
The most effective programs use a blended model combining VR with traditional methods.
2. What equipment do I need to get started with VR in medical education?
Requirements vary by platform, but typically include:
- A VR headset (standalone or PC-tethered)
- Hand controllers or compatible tracking devices
- Access to a VR software platform or institutional license
- Adequate space and internet bandwidth for safe and smooth use
Many institutions provide this equipment through simulation centers. For personal exploration, check whether your school offers educational discounts or device loans.
3. Are VR-based training outcomes supported by evidence?
Yes, a growing body of literature shows that VR can:
- Improve procedural skill performance compared to traditional methods alone
- Enhance knowledge retention and spatial understanding of anatomy
- Reduce time to competence for certain surgical and procedural skills
- Increase learner engagement and perceived self-efficacy
However, results vary by specialty, scenario design, and integration into the broader curriculum. Evidence is strongest where VR is carefully aligned with learning objectives and supplemented by debriefing.
4. Can VR help me prepare for residency or board exams?
VR can be a powerful adjunct, particularly for:
- Practicing OSCE-style clinical encounters and communication tasks
- Reinforcing anatomy, imaging interpretation, and procedural steps
- Running through emergency algorithms (ACLS, PALS, trauma protocols)
- Enhancing clinical reasoning with case-based simulations
Use VR alongside question banks, textbooks, and in-person clinical exposure—not as a stand-alone preparation tool.
5. What are the main limitations of VR that I should be aware of?
Key limitations include:
- Incomplete fidelity: While improving rapidly, VR still cannot perfectly replicate tactile feedback, nuanced physical findings, or complex human interactions.
- Access issues: Not all learners or institutions have equal access to hardware, software, and IT support.
- Motion sickness: A subset of users may experience discomfort, especially in early sessions.
- Content gaps: Some specialties and procedures may still have limited high-quality VR modules.
Understanding these constraints will help you use VR strategically and realistically within your broader training plan.
Virtual reality is rapidly becoming a cornerstone of technology in medicine and the future of healthcare training. For future physicians, embracing VR now is less about chasing novelty and more about preparing to practice—and lead—in a healthcare system where digital competence is as critical as clinical expertise.



















