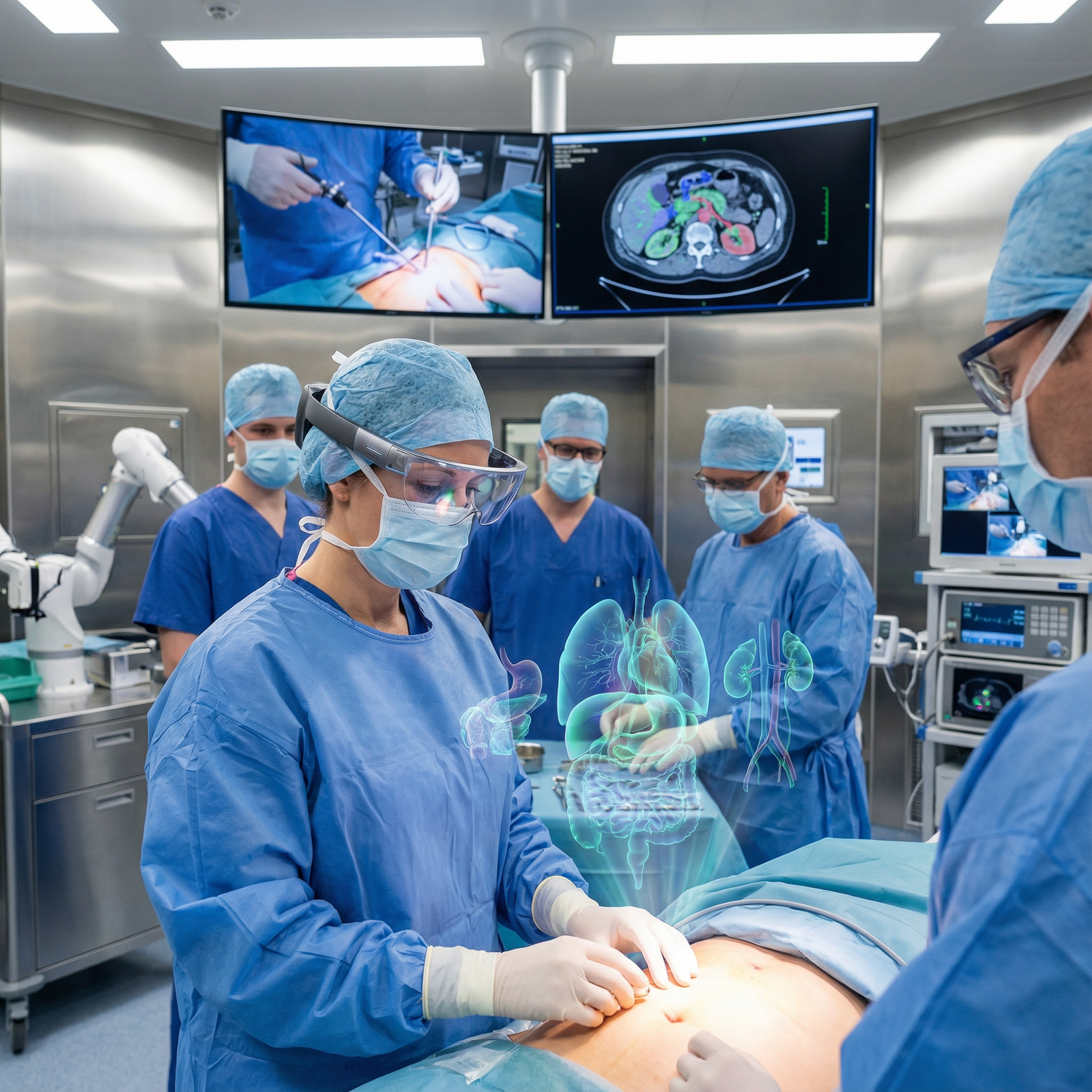
Introduction: Where Surgery Meets Digital Overlay
Augmented Reality (AR) has moved rapidly from science fiction and gaming into the core of medical technology. For surgeons, it represents one of the most practical and transformative healthcare innovations in the operating room.
Unlike purely theoretical tools, AR is already being piloted and deployed in real hospitals—particularly in orthopedics, neurosurgery, plastics, ENT, and interventional specialties. From 3D image-guided screw placement in the spine to tumor margin visualization in oncologic surgery, AR is starting to influence daily clinical decision-making.
At its core, augmented reality in surgery means overlaying relevant digital information—such as imaging, anatomical models, navigation cues, or procedural checklists—directly onto the surgeon’s view of the real operative field, in real time. Rather than forcing surgeons to repeatedly look away to external screens, AR aims to put the right information in the right place at exactly the right moment.
For medical students and residents, understanding AR is no longer optional “future tech”—it is becoming a core part of medical education and surgical training. This article explores how AR works in surgery, current and emerging applications, tangible benefits, key challenges, and what you can do now to prepare for this evolving landscape.
Understanding Augmented Reality in Surgery
AR vs VR: Why AR Fits the OR
It is important to distinguish Augmented Reality (AR) from Virtual Reality (VR):
- Virtual Reality (VR): Fully immerses the user in a computer-generated environment, blocking out the real world. Useful for simulation, preclinical training, and procedural rehearsal.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Keeps the real world visible but overlays digital content (e.g., images, labels, 3D models, navigation lines) on top of it. This is far better suited to live surgery, where situational awareness of the real patient and environment is critical.
Key Components of Surgical AR Systems
Most AR platforms used in surgery build on a common technical stack:
Display hardware
- Head-mounted displays (HMDs) like Microsoft HoloLens or specialized surgical AR headsets
- Transparent smart glasses
- Projector-based systems that display overlays directly onto the patient or onto the surgical field
- AR-enabled endoscopes and microscopes
Tracking and registration
- Optical or electromagnetic tracking systems
- Infrared markers, fiducials, or surface-matching methods
- Algorithms to align (register) preoperative imaging with the patient’s actual anatomy on the table
Software and visualization
- 3D reconstruction of CT/MRI/angiography data
- Customizable overlays (e.g., vessels, nerves, tumor margins, pedicle trajectories)
- Real-time updates as the surgeon or instruments move
When this system is well-calibrated, a surgeon looking through an AR display can see, for example, a tumor’s boundaries or vascular structures “inside” the patient, mapped with millimetric accuracy to the visible anatomy.
Key Applications of Augmented Reality in Surgery
1. Enhanced Visualization of Anatomical Structures
Improved visualization is the most intuitive and widely used AR application in surgery.
3D Visualization Without Invasiveness
Traditional 2D imaging can make complex anatomy difficult to grasp, especially in deformity, revision cases, or congenital anomalies. AR enables:
- True 3D understanding: Reconstructed CT or MRI scans converted into interactive 3D models that the surgeon can rotate, slice, and zoom in their field of view.
- Understanding spatial relationships: Clarifying the position of deep-seated tumors, vascular variants, or critical nerves relative to the planned incision or dissection path.
- Case planning brought into the OR: The same 3D models used in preoperative planning can be brought into the operating room and overlaid onto the patient for execution.
For example, in complex craniofacial reconstruction, AR can project a pre-planned bone-cutting guide and ideal reconstruction shape onto the skull, guiding the surgeon in real time.
Superimposing Imaging Data on the Surgical Field
One of the most powerful uses of AR is fusion of preoperative imaging with the live operative view:
- Overlaying CT/MRI onto the patient: Surgeons can “see through” tissue to underlying structures, such as:
- Intracranial lesions and key vessels in neurosurgery
- Bronchial or vascular anatomy in thoracic surgery
- Deep vascular malformations in plastic or ENT surgery
- Real-time adjustment: As the surgeon repositions or changes the angle of view, the overlay adjusts to stay aligned with the relevant anatomy.
This is particularly valuable in surgeries where millimeters matter, such as:
- Resection of brain tumors near eloquent cortex
- Skull base surgery where vital vessels and nerves are densely packed
- Liver surgery where respecting vascular and biliary anatomy is critical
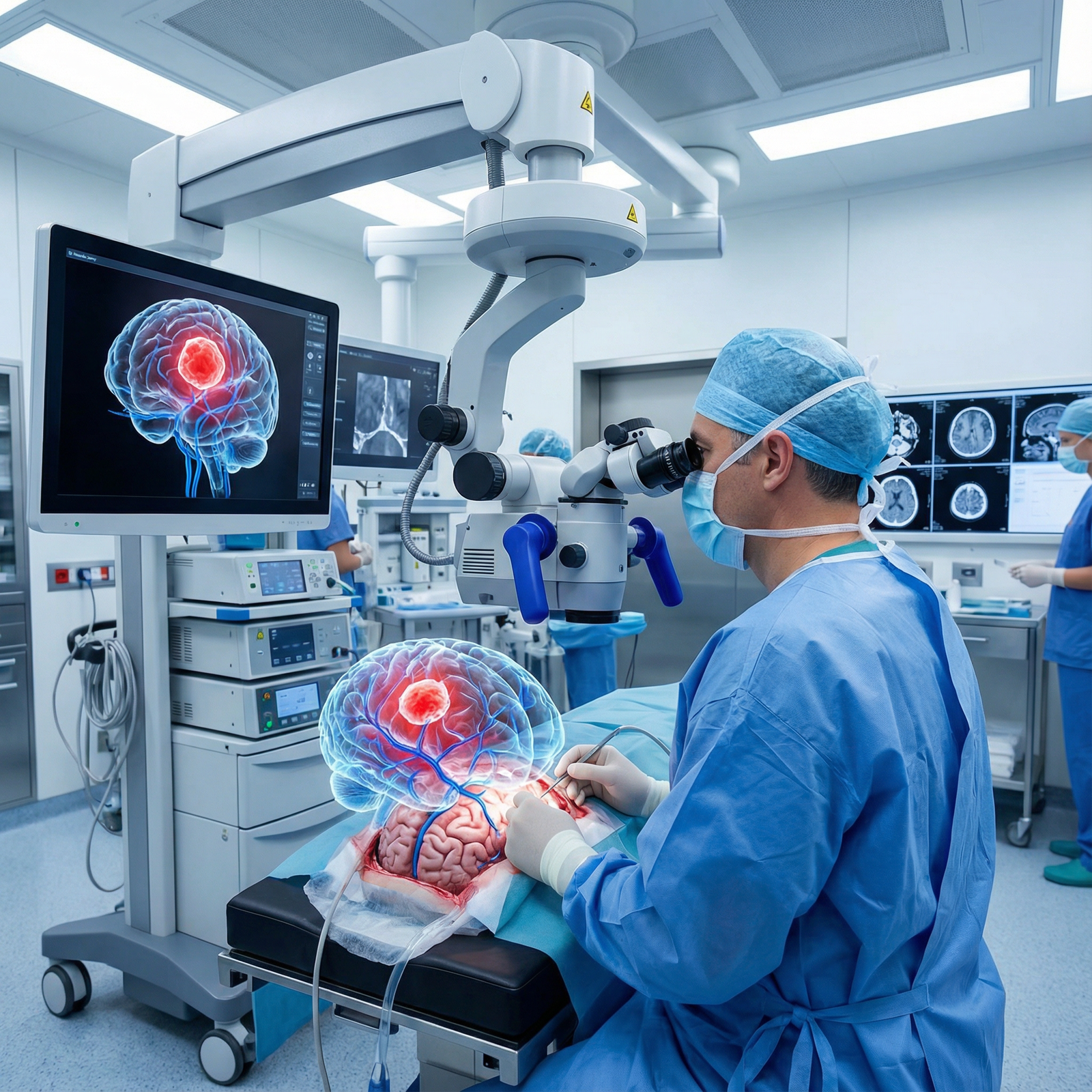
2. AR-Guided Surgical Navigation
AR can serve as an advanced “GPS” for the body, especially when combined with surgical navigation systems.
Orthopedic and Spine Surgery
In spine and orthopedic procedures, AR is increasingly used to guide implant placement:
Pedicle screw placement in spine surgery
- 3D trajectories for each screw overlaid on the vertebrae
- Surgeons see in real time where to drill and how deep, decreasing dependence on fluoroscopy
- Reduced radiation exposure for the team and more accurate instrumentation
Joint reconstruction
- Visual guidance for alignment angles and implant positioning in total knee or hip arthroplasty
- Better restoration of mechanical axes and joint biomechanics
These tools not only enhance precision but can shorten the learning curve for complex reconstructions.
Neurosurgical and ENT Navigation
Neurosurgeons and ENT surgeons already rely heavily on image-guided systems. AR extends this by:
- Integrating navigation directly into the microscope or endoscope view
- Overlaying target points, planned resection boundaries, or critical structures (e.g., carotid arteries, optic nerve)
- Reducing the need to repeatedly glance at separate navigation monitors
This blended view can keep the surgeon’s attention focused squarely on the operative field while still benefiting from precise image guidance.
3. Education, Training, and Simulation
For medical students and residents, AR is reshaping medical education and procedural training.
Interactive Anatomy and Procedure Learning
AR platforms (e.g., HoloLens-based systems, tablet AR apps) allow trainees to:
- Explore fully interactive 3D anatomy
- Peel back layers of tissue virtually (skin → muscle → bone → vessels → organs)
- View common variants and pathology superimposed on “standard” models
- Practice identifying structures as if in a real OR
Instead of passive reading or 2D atlases, learners can manipulate digital cadavers or patient-specific models and immediately translate that understanding into the operating room.
AR-Based Procedural Rehearsal
Residents can rehearse a procedure step-by-step using AR:
- Projecting a procedural roadmap over a simulator or physical model
- Receiving visual prompts for key steps and safety checks (e.g., structure identification, ligation points)
- Practicing multiple “what if” scenarios (e.g., variant anatomy, intraoperative bleeding) without risk to patients
This immersive rehearsal can be especially valuable before:
- First-time or rare procedures
- Complex oncology resections
- Minimally invasive techniques with steep learning curves
4. Real-Time Collaboration and Remote Guidance
AR also transforms how surgeons and teams collaborate.
Intraoperative Team Collaboration
Within the OR, AR enables:
- Shared visualization of the same overlay among multiple team members
- Ability for a lead surgeon to annotate the field (e.g., “dissect here,” “avoid this area”) and have annotations appear in everyone’s view
- Clearer communication between surgeon, assistant, and scrub nurse about instruments, steps, and hazards
This can be particularly helpful for teaching cases or complex procedures involving multiple subspecialists.
Remote Mentoring and Telepresence
In global surgery and telemedicine, AR opens powerful possibilities:
- An expert surgeon in another city—or another country—can:
- See what the local surgeon sees (via AR headset feed)
- Draw guidance arrows, highlight structures, or mark safe zones that appear in the operating surgeon’s field of view
- Offer verbal guidance in real time, effectively “scrubbing in” virtually
For low-resource settings or new programs, this can accelerate skill transfer and improve safety while avoiding the cost and logistics of physical travel.
5. Postoperative Assessment and Patient Engagement
AR remains useful after the procedure is over.
Postoperative Review and Quality Improvement
Surgeons can use AR tools to:
- Compare planned vs. actual implant placement or resection margins
- Overlay postoperative imaging on intraoperative views to analyze accuracy
- Systematically review complex cases for quality improvement and education
This promotes data-driven refinement of technique and can support research on surgical outcomes.
Patient Education and Shared Decision-Making
AR is also a powerful communication tool with patients:
- Preoperative: Show patients a 3D model of their own anatomy and demonstrate the planned surgical steps, risks, and alternatives.
- Postoperative: Visualize what was done (e.g., “Here is where we placed the screws; here is the tumor we removed.”)
This increases patient understanding, supports informed consent, and may improve trust and satisfaction.
Benefits of Augmented Reality in Surgical Practice
1. Increased Precision and Safety
The most immediate benefit is improved accuracy:
- More precise localization of tumors, vessels, nerves, and functional areas
- Reduced risk of damaging critical structures
- Better alignment and positioning of implants or grafts
Multiple early studies have demonstrated reduced error in pedicle screw placement, improved resection margins, and improved anatomical targeting when AR is used as an adjunct.
2. Reduced Operative Time and Radiation
With the right implementation, AR can streamline workflow:
- Fewer stops to interpret external screens or re-check landmarks
- Less reliance on repeated fluoroscopy (especially in orthopedics and interventional radiology)
- Faster and more confident instrument placement
Shorter operative times can translate into:
- Lower anesthesia exposure
- Reduced infection risk
- More efficient OR utilization, a critical operational and economic advantage
3. Enhanced Training Efficiency and Skill Acquisition
For trainees:
- AR supports deliberate practice through simulation and rehearsal
- Complex 3D anatomy becomes more intuitive
- Feedback can be immediate and visual, reinforcing correct technique
For attendings supervising residents or fellows, AR can:
- Make their “mental map” of the case visible and shareable
- Support graded responsibility by providing visual safety nets for more junior surgeons
4. Improved Patient Engagement and Satisfaction
Patients often struggle to understand 2D imaging or abstract descriptions. AR tools can:
- Make pathology and planned treatment visible and concrete
- Help patients visualize the trajectory of recovery (e.g., how deformity will be corrected)
- Increase adherence to care plans by improving understanding
In an era where patient-centered care and shared decision-making are central, AR offers a highly intuitive means of communication.
5. Catalyst for Broader Healthcare Innovation
Finally, AR in surgery does not exist in isolation. It acts as a bridge between:
- Imaging,
- Artificial intelligence,
- Robotic surgery, and
- Digital health records.
As data becomes more seamlessly integrated across platforms, AR will be the interface that presents this information to surgeons in a cognitive-friendly, actionable way.
Challenges and Limitations of AR in Surgery
Despite its promise, AR in surgery faces real barriers that residents and clinicians should understand.
1. Cost and Resource Requirements
AR systems often require:
- High-end hardware (headsets, cameras, trackers)
- Powerful computing infrastructure and network connectivity
- Integration with PACS, EHRs, and OR hardware
- Ongoing maintenance and software updates
This can be prohibitive for:
- Smaller hospitals
- Institutions in low- and middle-income countries
- Programs with limited capital budgets
Value-based analysis and evidence of improved outcomes will be critical to justifying investment.
2. Technical Limitations and Reliability
Key technical challenges include:
- Registration accuracy: Misalignment of overlays by even a few millimeters can be dangerous in delicate surgery.
- Latency: Any lag between movement and overlay adjustment can create disorientation or inaccuracy.
- Field-of-view constraints: Some headsets provide limited viewing areas, forcing unnatural head movements.
- Ergonomics: Comfort, weight, and sterility considerations are essential during long operations.
For clinical acceptance, AR must be:
- Highly reliable
- Intuitive to use
- Non-disruptive to existing workflows
3. User Acceptance and Learning Curve
Some surgeons may be skeptical or resistant:
- Concern that AR could distract or overwhelm attention
- Perception that traditional methods (landmarks, fluoroscopy, experience) are adequate
- Time constraints in an already overloaded clinical schedule
Successful implementation often requires:
- Champions within the department
- Human factors–informed interface design
- Adequate training, including simulation before real cases
- Choosing early use-cases where benefits are obvious (e.g., deformity, revision, or complex cases)
4. Data Privacy, Cybersecurity, and Regulatory Issues
AR involves capturing and processing sensitive data:
- Live video feeds of the OR and patient
- Integration with identifiable imaging and EHR data
- Cloud-based processing in some systems
This raises questions about:
- HIPAA/GDPR compliance in different jurisdictions
- Secure transmission and storage of data
- Regulatory approval (FDA, EMA, etc.) as medical devices, especially for systems that guide decisions
Institutions adopting AR must involve IT, legal, and compliance teams early.
The Future of Augmented Reality in Surgery and Medical Education
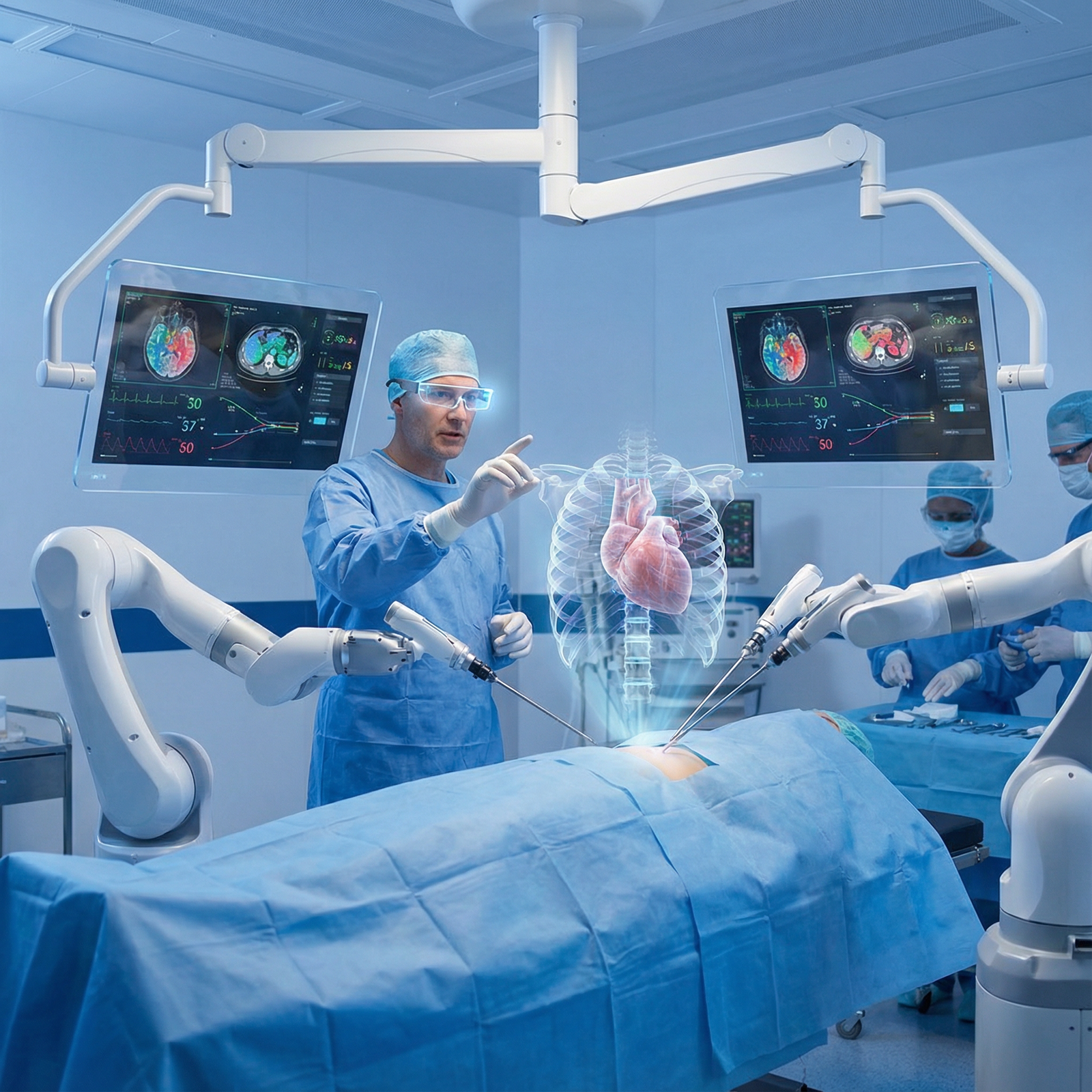
Looking ahead 5–10 years, AR is likely to become deeply embedded in surgical care and medical education, interacting closely with other healthcare innovations.
1. More Advanced, Integrated AR Systems
We can expect:
- Lighter, more comfortable headsets with wider fields of view
- Better depth perception and more natural color/contrast blending with the real world
- Seamless integration with:
- Robotic surgery consoles
- Surgical microscopes and endoscopes
- Intraoperative imaging (e.g., cone-beam CT, ultrasound, fluorescence imaging)
As AR becomes standard in major OR platforms, it will feel less like an “add-on gadget” and more like a built-in part of the surgical environment.
2. Synergy with Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The combination of Augmented Reality and AI is particularly powerful:
- AI-enhanced image segmentation: Faster, more accurate identification of tumors, vessels, or anatomical planes for overlay.
- Predictive analytics: AI models suggesting optimal resection planes or instrumentation based on population data plus patient-specific anatomy.
- Context-aware assistance: The AR system recognizing the step of the procedure and presenting relevant checklists, alerts, or warnings automatically.
This could lead to intelligent, adaptive AR that supports the surgeon without being intrusive.
3. Expansion of Telemedicine and Global Surgery
AR-based remote guidance is well-positioned to:
- Support global health and capacity-building in under-resourced settings
- Enable experts to supervise complex cases remotely
- Reduce geographic disparities in access to specialized surgical care
As network bandwidth and latency improve, remote AR collaboration will become more seamless and routine.
4. Routine Integration into Training Programs
For medical students, residents, and fellows:
- AR anatomy and procedural modules will become staples of curricula
- “AR labs” may supplement or partially replace traditional cadaver labs in some institutions
- Case-based AR simulations will be used to assess competence and readiness for independent practice
Familiarity with AR tools will become an expected skill rather than a niche interest.
5. Patient-Facing AR Applications
Beyond the OR, we may see:
- At-home AR apps that let patients visualize their pathology and planned surgeries with their smartphones or AR glasses
- Physical therapy and rehabilitation AR programs guiding exercises and visualizing progress
- AR in outpatient clinics to enhance explanations and counseling
These tools can strengthen patient engagement and truly “democratize” complex medical information.
Practical Tips for Residents and Early-Career Surgeons
If you are in training or early practice, you can begin preparing now:
- Seek exposure: Ask to observe or participate in cases using AR navigation or visualization.
- Engage in research: Join or initiate projects evaluating AR accuracy, workflow impact, learning outcomes, or cost-effectiveness.
- Leverage AR for studying: Use AR-enabled anatomy and radiology apps to solidify 3D understanding.
- Give feedback: When your department trials AR systems, provide user feedback focused on ergonomics, workflow, and cognitive load.
- Stay up to date: Follow literature on AR in your specialty and attend sessions on digital surgery at major conferences.
Your generation will shape how AR is implemented, standardized, and refined—your perspective is crucial.
FAQ: Augmented Reality in Surgery and Medical Education
1. What exactly is augmented reality in surgery?
Augmented reality in surgery is the use of technology to overlay digital information—such as 3D anatomical models, imaging data, or navigation cues—onto the surgeon’s real view of the patient and operative field. This can be delivered through headsets, AR-enabled microscopes, monitors, or projectors, and is updated in real time as the surgeon or patient moves.
2. How does AR improve surgical precision and safety?
AR enhances precision by:
- Providing accurate 3D visualization of hidden structures (e.g., vessels, nerves, tumor margins)
- Guiding instrument trajectories (e.g., pedicle screws, biopsies) with virtual paths
- Reducing misinterpretation of 2D imaging and anatomical landmarks
- Allowing rapid confirmation of where you are operating relative to critical anatomy
This can reduce complications, improve implant placement, and increase the likelihood of complete, safe resections.
3. What AR tools are currently used in real operating rooms?
Current tools include:
- AR-enhanced surgical navigation systems for spine, orthopedics, and neurosurgery
- Headsets like Microsoft HoloLens adapted for preoperative planning and intraoperative guidance
- AR-enabled microscopes that overlay tumor or vascular maps on the microscopic view
- AR systems integrated into robotic platforms or fluoroscopy units
Most are still in early or mid-stage adoption, often in high-resource centers or within clinical trials.
4. What are the main challenges to widespread adoption of AR in surgery?
Key challenges include:
- High upfront and maintenance costs
- Ensuring millimetric registration accuracy and minimal latency
- Designing ergonomic, sterile, and comfortable devices
- Overcoming user skepticism and learning curves
- Addressing data privacy, cybersecurity, and regulatory requirements
Demonstrating clear outcome benefits and cost-effectiveness will be essential for broader uptake.
5. How can medical students and residents benefit from AR right now?
Trainees can:
- Use AR anatomy applications to build robust 3D spatial understanding
- Practice procedures in AR-enhanced simulation labs before performing them on patients
- Participate in AR-assisted cases to see how imaging and planning integrate with live surgery
- Engage in AR-related research and innovation projects, helping shape future clinical workflows
By becoming fluent in AR early, you’ll be better prepared for a surgical landscape where digital overlays and medical technology are integral—not optional—parts of practice.
Bottom line: Augmented Reality in surgery is more than a buzzword—it is a rapidly maturing healthcare innovation with real potential to improve precision, safety, education, and patient engagement. As technology, AI, and surgical practice continue to converge, AR will play a central role in defining the future of healthcare and the next generation of surgical care.



















