
What to Expect When Applying for Your IMG Visa: H-1B vs. J-1
As an International Medical Graduate (IMG), deciding how to enter U.S. residency or fellowship training is one of the most important steps in your career. Beyond USMLE scores, clinical experience, and residency interviews, you must also navigate U.S. Immigration rules and choose the right IMG visa path—most commonly the H‑1B or J‑1.
Both visas can support you through U.S. graduate medical education, but they differ significantly in eligibility, long‑term impact, and flexibility. Understanding these differences early—ideally before ERAS applications—can help you target programs strategically and avoid surprises later.
This guide walks you through what to expect when applying for either an H‑1B or J‑1 visa as an IMG, including requirements, timelines, pros and cons, and practical tips from a residency applicant’s perspective.
Overview of Visa Options for IMGs in U.S. Medical Residency
Why Visa Choice Matters for IMGs
Your visa type affects much more than your entry into residency. It can shape:
- Where you can train and later work
- Whether you must return to your home country
- How easily you can apply for a green card
- Your spouse’s ability to work in the U.S.
- Long‑term career planning (academic vs community, underserved vs urban settings)
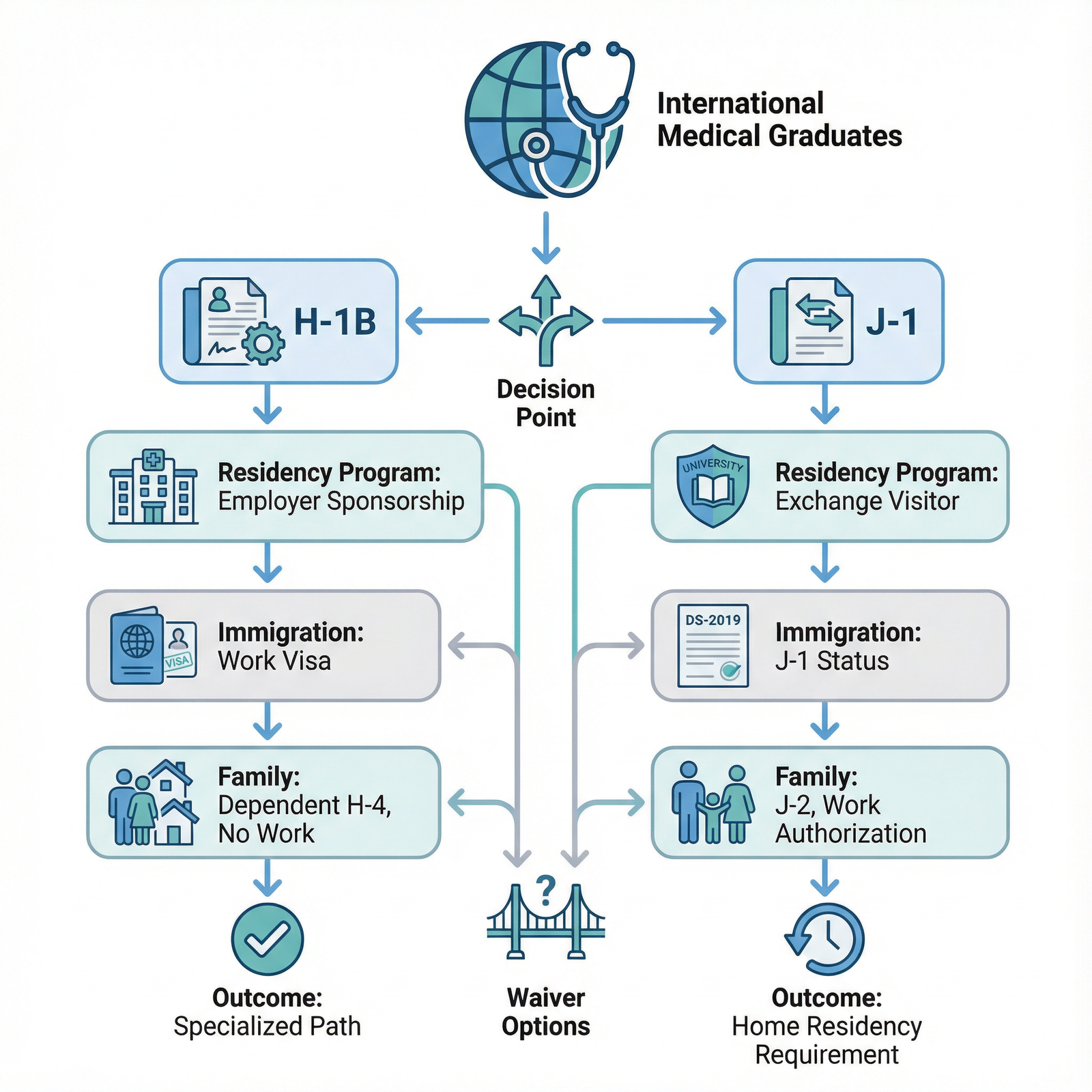
Most IMGs in U.S. residency use one of two routes:
- J‑1 Exchange Visitor Visa (for Clinical Training)
- H‑1B Specialty Occupation Visa (for Physician Employment)
Some programs are J‑1 only, a smaller number are H‑1B friendly, and a few support either option. Understanding both up front helps you ask the right questions during interviews and program communications.
The H‑1B Visa for IMGs in Residency and Fellowship
The H‑1B visa is a non‑immigrant visa that allows U.S. employers to temporarily employ foreign professionals in “specialty occupations.” For IMGs, your employer is usually the hospital or academic medical center where you match.
Key Characteristics of the H‑1B Visa
- Occupation: “Physician” in a specialty occupation
- Purpose: Employment for professional services (e.g., residency, fellowship, attending physician role)
- Intent: Dual intent—you may pursue permanent residency while in H‑1B status
Core Features of H‑1B for Medical Graduates
Duration
- Typically approved in increments up to three years
- Maximum standard stay: six years, with some exceptions if you are in the green card process
- Time spent on H‑1B in residency counts toward the six‑year total, which can matter if you plan a long fellowship sequence
Employer Sponsorship
- Your residency or fellowship program files the petition; you cannot self‑petition
- The employer must show:
- You meet state licensing/permit requirements
- You are qualified for the physician position
- They will pay at least the “prevailing wage” set by the Department of Labor
Dual Intent Advantage
- You may:
- Begin an employment‑based green card process (e.g., EB‑2, EB‑1) during training or afterward
- Adjust status to permanent residency from within the U.S.
- This makes H‑1B especially attractive for IMGs who are confident they want to build a long‑term career in the U.S.
- You may:
Dependent Visas (H‑4)
- Spouse and unmarried children under 21 can accompany you on H‑4
- Work authorization for H‑4 dependents:
- Possible in some cases if you are far enough along in your green card process
- Rules can change; always verify current U.S. Immigration policy
Eligibility Requirements for H‑1B as an IMG
Most programs that sponsor H‑1B for residency/fellowship will expect the following:
ECFMG Certification
- Must be fully certified (including passing USMLE Steps and credential verification)
USMLE Step Requirements
- Typically: Passed USMLE Step 1, Step 2 CK
- Step 3 completion is often required before filing the H‑1B petition (this is a key difference from J‑1)
- This means you may need to:
- Plan Step 3 early (often by fall–winter of your PGY‑1 year if switching from J‑1 is considered, or pre‑residency if going directly to H‑1B)
- Check each program’s specific policy
State License or Training Permit
- Each state has its own requirements:
- Some allow trainees to work on a training license without Step 3
- Others require Step 3 for licensure or permit
- Your program’s immigration office will guide you, but you should research state rules as you shortlist programs
- Each state has its own requirements:
H‑1B Application Process for IMGs
The H‑1B process is employer‑driven. In medical training, teaching hospitals often file cap‑exempt H‑1B petitions (not subject to the general H‑1B lottery), which is a major benefit for IMGs.
Typical steps:
Match or Job Offer
- Match to a residency or fellowship program that explicitly sponsors H‑1B visas
- Clarify visa support early—ideally before ranking programs
Labor Condition Application (LCA)
- Program submits an LCA to the U.S. Department of Labor
- Confirms:
- Wage level
- Work conditions
- That hiring you will not adversely affect similarly employed U.S. workers
H‑1B Petition (Form I‑129)
- Employer files Form I‑129 with USCIS along with:
- Contract / offer letter
- LCA approval
- Evidence of your credentials (ECFMG, degree, USMLE, license/permit)
- Some institutions use premium processing (extra fee for faster USCIS decision)
- Employer files Form I‑129 with USCIS along with:
Consular Processing / Visa Interview
- Once approved, you:
- Complete DS‑160, schedule an appointment at a U.S. consulate
- Attend an H‑1B visa interview and present your approval notice and supporting documents
- If you are already in the U.S. in another status, your status may be changed without travel, depending on your situation
- Once approved, you:
The J‑1 Visa for Clinical Training: The Default Path for Many IMGs
The J‑1 Exchange Visitor Visa for physicians is specifically designed for international medical graduates coming for graduate medical education or training. It is administered in partnership with ECFMG, which acts as your J‑1 program sponsor.
Key Characteristics of the J‑1 Visa for IMGs
- Purpose: Educational exchange and clinical training
- Administered by: U.S. Department of State and ECFMG (as sponsor)
- Common Use: The most frequently used visa for IMGs in residency and fellowship
Core Features of J‑1 for Medical Training
Duration
- Typically covers the entire length of your approved training program
- Renewable annually, as long as:
- The training remains progressive
- You have satisfactory evaluations
- There is usually a maximum time limit for clinical training (commonly seven years, with exceptions)
Sponsorship
- You must be sponsored by ECFMG for clinical J‑1 status
- Your residency/fellowship program must be an ACGME‑accredited training site
- The institution and ECFMG coordinate to issue your Form DS‑2019
Two‑Year Home Country Residence Requirement (INA §212(e))
- After completing training, most J‑1 physicians are required to:
- Return to their home country for at least two years cumulatively, OR
- Obtain a waiver of this requirement
- Until this is satisfied or waived, you typically cannot:
- Change status to H‑1B or L‑1 from within the U.S.
- Receive certain types of immigrant visas or green cards
- After completing training, most J‑1 physicians are required to:
Dependent Visas (J‑2)
- Spouse and unmarried children under 21 can enter as J‑2 dependents
- J‑2 holders may apply to USCIS for work authorization (EAD) and, once approved, can work in most types of jobs
Eligibility Requirements for J‑1 as an IMG
Compared to H‑1B, the J‑1 is often more accessible for first‑time IMGs entering residency.
Typical requirements include:
ECFMG Certification
- Must be certified by ECFMG (or on track if starting the process)
USMLE
- Pass USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 CK (or COMLEX equivalent for DO graduates)
- Step 3 is not required for J‑1 sponsorship, which is a major difference from H‑1B
Pre‑arranged Training Position
- You must have a confirmed spot in an ACGME‑accredited residency or fellowship program
Home Country Ties
- Because of the exchange purpose, consular officers and the Department of State often look for evidence that you maintain ties to your home country (family, property, professional connections), although the 212(e) rule itself already envisions you returning
J‑1 Application Process for IMGs
The J‑1 process involves your training program, ECFMG, and the U.S. consulate.
Match or Acceptance
- Match into a J‑1‑sponsoring residency or obtain a fellowship position
- Program confirms it will support your J‑1 sponsorship through ECFMG
ECFMG J‑1 Sponsorship Application
- You submit an online application and supporting documents to ECFMG
- ECFMG verifies your:
- Credentials
- Training offer
- Funding
- Health insurance arrangements
Form DS‑2019 Issuance
- Once approved, ECFMG issues Form DS‑2019, your official document for J‑1 status
- Your program will often provide guidance and timing details
Consular Processing / Visa Interview
- You complete Form DS‑160 online
- Pay the SEVIS fee
- Schedule and attend a J‑1 visa interview at a U.S. embassy or consulate
- If approved, the J‑1 visa is placed in your passport
Head‑to‑Head Comparison: H‑1B vs. J‑1 for IMGs
Choosing between H‑1B and J‑1 depends largely on your career goals, timeline, and personal circumstances. Below is a practical comparison focused on issues that matter to residency and fellowship applicants.
Eligibility and Requirements
| Feature | H‑1B Visa | J‑1 Visa (Clinical Training) |
|---|---|---|
| Degree | Medical degree from accredited institution | Medical degree from accredited institution |
| Certification | ECFMG certification | ECFMG certification |
| Exams | Step 1, Step 2 CK, often Step 3 required | Step 1, Step 2 CK; Step 3 not required |
| Sponsorship | U.S. employer (hospital/program) | ECFMG as J‑1 sponsor; program must support J‑1 |
| Licensing/Permit | Must meet state rules (often more stringent) | Training license/permit per state |
| Specialty Occupation | Yes—physician role qualifies | Yes—specifically for medical training |
Application Complexity and Timing
H‑1B
- Often requires more lead time due to Step 3, LCA, and USCIS petition
- Many programs prefer to sponsor H‑1B for fellows or advanced trainees rather than interns
- Premium processing can speed approval but adds cost (usually paid by the institution)
J‑1
- Typically faster to process once you match
- Centralized through ECFMG, which streamlines many IMGs’ experience
- More widely used and familiar to GME offices
Cost Considerations
H‑1B Costs
- Filing fees can be substantial (commonly $1,500–$6,000+ depending on size of employer and options)
- By law, key H‑1B costs are generally paid by the employer, not the trainee
- You may pay for:
- Personal document procurement
- Visa interview fees
- Travel
J‑1 Costs
- Lower government filing fees than H‑1B
- However, expect:
- ECFMG sponsorship fees
- SEVIS fee
- Required health insurance for you and dependents at specified coverage minimums
- Budget in the range of $500–$1,500 plus travel and local consular fees, depending on your situation
Health Insurance Requirements
H‑1B
- Most residency/fellowship programs provide group health insurance
- No additional visa‑specific mandate beyond standard employer policies
J‑1
- Mandatory minimum coverage set by the U.S. Department of State
- You must maintain:
- Specified minimum medical coverage
- Repatriation of remains coverage
- Medical evacuation coverage
- Failure to maintain appropriate coverage can jeopardize your status
Impact on Long‑Term U.S. Immigration Plans
This is often the deciding factor for many IMGs.
H‑1B and Long‑Term Plans
- Dual intent allows:
- Starting a green card process during or after training
- Transition from residency → fellowship → attending role on H‑1B, then green card
- No automatic requirement to return to your home country
- Dual intent allows:
J‑1 and the Two‑Year Home Residence Requirement
- The two‑year return rule can delay or complicate:
- Transition to H‑1B or permanent residency
- Long‑term employment in the U.S.
- However, J‑1 waivers are possible through:
- Conrad 30 programs (state health departments; usually require working in underserved areas for 3 years on H‑1B)
- Federal government agencies (e.g., VA, HHS, DoD) that show a public interest need
- Hardship or persecution claims (if returning home would cause exceptional hardship or persecution)
- For many J‑1 IMGs, the realistic path to staying in the U.S. post‑training involves:
- Securing a J‑1 waiver job (often in rural or underserved communities)
- Working there for 3 years on H‑1B
- Pursuing a green card during or after that period
- The two‑year return rule can delay or complicate:
Cultural and Professional Adaptation (For Both Visa Types)
Regardless of whether you choose an H‑1B or J‑1, you will need to adapt to U.S. medical culture:
- Communication
- Patient‑centered communication, shared decision‑making, documentation standards
- Team Dynamics
- Interdisciplinary teams, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, pharmacists
- Cultural Competence
- Caring for diverse patient populations with varying beliefs, health literacy, and expectations
Your visa status does not define your clinical abilities, but it can influence:
- Where you can work (e.g., underserved areas for J‑1 waiver jobs)
- How long you can stay
- How easily you can change employers after training
Case Example: Navigating the J‑1 Path
Imagine an IMG from India who matches into an internal medicine residency on a J‑1 visa:
- During PGY‑2, they decide they want to build a long‑term career in the U.S.
- They complete residency and a fellowship on J‑1 sponsorship.
- At graduation, they are subject to the two‑year home requirement.
- To remain in the U.S., they:
- Apply for a Conrad 30 J‑1 waiver in a medically underserved area
- Obtain a job offer from a hospital willing to sponsor an H‑1B waiver position
- After three years of service, they are free of the J‑1 obligation and can pursue a green card
Planning this trajectory early in training—ideally before fellowship—helps avoid last‑minute panic and missed opportunities.

Practical Advice for Choosing Between H‑1B and J‑1 as an IMG
1. Clarify Your Long‑Term Career Goals
Ask yourself:
- Do I definitely want to stay in the U.S. long‑term?
- Am I open to working in rural or underserved areas after training?
- Am I considering returning to my home country eventually?
If you are strongly committed to a long‑term U.S. career and don’t want the constraint of a two‑year home requirement, an H‑1B (when available) is often preferable.
If you are flexible, uncertain, or aiming primarily for training experience before returning home, J‑1 can be a straightforward path.
2. Check Each Program’s Visa Policies Early
Program policies vary widely:
- Some are J‑1 only and will not sponsor H‑1B for residents
- Some support H‑1B for fellows only
- A smaller group is H‑1B friendly even for PGY‑1s
Before you spend money on applications, review program websites and, if unclear, email the program coordinator or GME office with specific questions:
- “Do you sponsor H‑1B visas for categorical residents?”
- “Is USMLE Step 3 required prior to H‑1B filing?”
- “Do you accept J‑1 candidates only?”
Use this information to target your ERAS list strategically.
3. Plan Your USMLE Timeline Around Visa Options
If H‑1B is your goal:
- Aim to complete USMLE Step 3 early:
- Some IMGs take Step 3 before starting residency to keep the H‑1B option open
- Others take it during the first year, especially if considering a change from J‑1 to H‑1B for fellowship or attending roles
- Be aware of each state’s Step 3 and licensing rules
If J‑1 is likely:
- Focus on solid Step 1 and Step 2 CK performance, clinical experience, and strong applications
- Step 3 becomes more time‑flexible (but still important for later licensing and career mobility)
4. Consider Your Family’s Needs
For married IMGs or those with children, visa choice also affects your family:
Spouse’s Work Options
- H‑4: Limited work options, tied to your green card process progress
- J‑2: Can apply for work authorization (EAD) and, once approved, work in a variety of jobs
Education and Schooling
- Both H‑4 and J‑2 children can enroll in U.S. schools
- Stability may depend on the length and type of your training and any waiver obligations
5. Get Professional Legal Guidance When Needed
While residency GME offices and ECFMG provide excellent support, they do not replace individualized legal advice. Consider consulting an experienced immigration attorney if:
- You have complex immigration history
- You are transitioning from J‑1 to H‑1B after a waiver
- You’re starting a green card process during fellowship or early attending years
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About IMG Visas: H‑1B vs. J‑1
1. Which visa is “better” for IMGs: H‑1B or J‑1?
It depends on your situation:
H‑1B may be better if:
- You are certain you want a long‑term career in the U.S.
- You can complete USMLE Step 3 in time
- You match at a program willing to sponsor H‑1B
- You want maximum flexibility for future green card options
J‑1 may be better if:
- Your priority is simply securing U.S. training, and most of your target programs are J‑1 only
- You are open to returning home after training or working in underserved areas under a waiver
- You don’t yet have Step 3 and want to start residency as soon as possible
There is no universal “best”; it’s about aligning visa choice with your career, immigration, and family goals.
2. Can I apply for both H‑1B and J‑1 at the same time?
Technically, some IMGs explore both options (e.g., match to a program that offers both, then decide). However:
- Programs typically prefer a single clear plan
- Conflicting applications can create confusion during immigration processing
- Your program and GME office will guide you toward the most feasible option
In practice, you should prioritize one path based on program policy, Step 3 status, and your long‑term goals.
3. How long does visa processing take for H‑1B and J‑1?
Timelines vary by year and consulate workload, but generally:
- H‑1B
- LCA and USCIS processing can take weeks to several months
- Premium processing can shorten USCIS review to 15 calendar days, but consular appointment availability still matters
- J‑1
- ECFMG processing for sponsorship plus consular appointment can often be completed within a few weeks to a couple of months once all documents are ready
Because start dates for residency are fixed (usually July 1), programs and GME offices are experienced at planning ahead. Still, submit required documents promptly to avoid delays.
4. Are there any countries exempt from the J‑1 two‑year home residence requirement?
In some cases, the two‑year requirement applies specifically to:
- Citizens or permanent residents of certain countries for which the U.S. has funded exchange programs
- Individuals whose training is funded by their home government or international organizations
- Individuals whose specialty appears on their country’s skills list
Some countries have no applicable skills list, which may affect how 212(e) is applied, but most J‑1 physicians are subject to the two‑year rule. Because this is complex and fact‑specific, review:
- Your DS‑2019
- The visa stamp in your passport
- Guidance from an immigration attorney if uncertain
5. Can I switch from J‑1 to H‑1B or vice versa during or after residency?
Yes, but with important conditions:
J‑1 → H‑1B
- If you are subject to the two‑year home residence rule (most J‑1 IMGs are), you generally must complete or waive this requirement before changing to H‑1B for long‑term employment
- A common route is completing residency/fellowship on J‑1, then obtaining a J‑1 waiver job on H‑1B and working 3 years in an underserved area
H‑1B → J‑1
- Less common but possible in some cases (for example, moving from employment into a pure training program)
- Requires coordination between GME, ECFMG, and immigration counsel; evaluate potential impacts on your H‑1B time limit and green card plans
Because these transitions are nuanced, they should be planned early and ideally discussed with an immigration lawyer plus your GME office.
Final Thoughts: Strategically Navigating IMG Visa Options
Choosing between H‑1B and J‑1 for U.S. medical residency is both an immigration decision and a career strategy decision. Both visas can successfully support your training; the key differences lie in:
- Entry requirements (especially USMLE Step 3 for H‑1B)
- Post‑training obligations (two‑year home residency for J‑1)
- Flexibility for long‑term U.S. Immigration (dual intent advantage for H‑1B)
- Where and how you can work after residency, particularly if you pursue a J‑1 waiver
As you plan your path:
- Research program visa policies before applying.
- Align your exam schedule (especially Step 3) with your preferred visa option.
- Discuss visa issues openly with program coordinators and GME offices.
- Seek professional immigration advice when your situation is complex or high‑stakes.
With careful planning and a clear understanding of H‑1B vs. J‑1 differences, you can choose the IMG visa path that best supports your training experience and your long‑term goals in U.S. medicine.





















