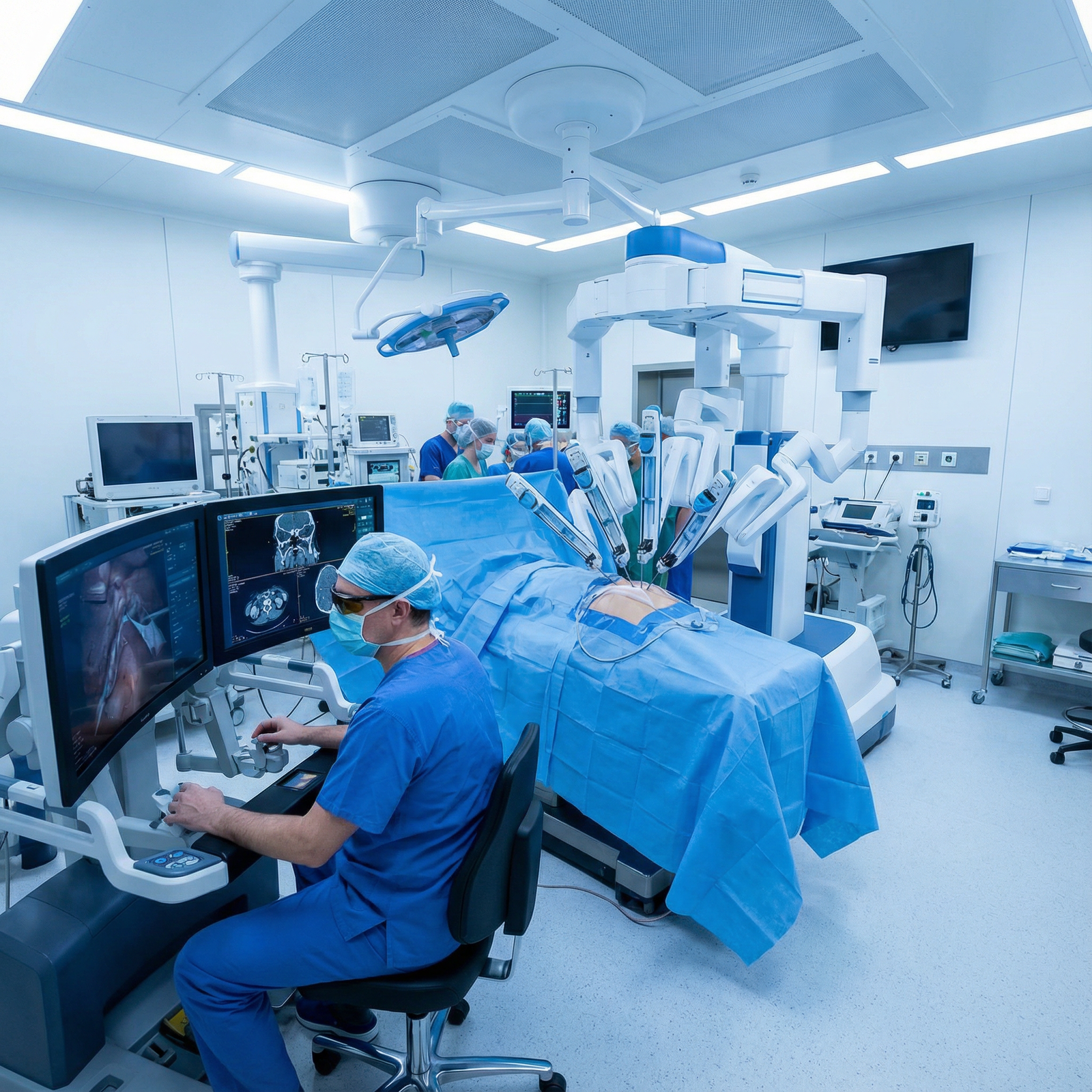
Introduction: How Robotics Is Redefining Modern Surgery
Robotic Surgery has transformed from experimental innovation to everyday practice in many operating rooms worldwide. For residents, fellows, and early-career surgeons, understanding this technology is no longer optional—it is central to how surgical care is delivered, evaluated, and reimbursed.
Robotic systems have expanded what Minimally Invasive Techniques can achieve, enabling surgeons to perform highly complex procedures through small incisions with unprecedented Surgical Precision. This evolution directly affects Patient Outcomes: shorter hospital stays, less pain, lower complication rates, and often faster returns to normal function.
This article provides a deep dive into the role of robotics in surgery, with a practical lens for those on the path to independent practice. We will review how the systems work, where they are used, the evidence supporting their benefits and limitations, and how Robotics and broader Healthcare Technology are reshaping surgical training and the post-residency job market.
Understanding Robotic Surgery: Core Concepts and System Components
Robotic surgery—more accurately termed “robotic-assisted surgery”—does not replace the surgeon. Instead, it augments the surgeon’s abilities through advanced visualization, motion scaling, and instrument dexterity.
In a typical robotic procedure, the surgeon sits at a console, manipulating hand controls and foot pedals. These inputs are translated into refined movements of robotic arms that hold instruments and a camera inside the patient. The result is enhanced control, stability, and access to areas that are difficult to reach with traditional open or even standard laparoscopic approaches.
Key Components of Robotic Surgical Systems
Most robotic platforms in use today share several core components:
Patient-Side Robotic Arms
- Multiple arms (often 3–4) are docked to the patient via trocars.
- Each arm can hold specialized instruments (e.g., needle drivers, scissors, bipolar clamps, staplers).
- Instruments often have “wristed” tips that mimic or exceed the degrees of freedom of the human wrist, allowing 540° or more of rotation and fine articulation.
- Motion scaling translates large hand movements at the console into tiny, precise movements inside the patient.
Surgeon Console
- The console is where the primary surgeon controls the system.
- Ergonomic controls reduce fatigue during long cases—an important but often overlooked benefit for surgical performance.
- A stereoscopic viewer provides 3D, high-definition, magnified images of the operative field.
- Foot pedals allow control of energy devices, camera movement, switching between arms, and clutching (resetting hand positions).
Vision and Camera Systems
- High-definition 3D endoscopes give a magnified, immersive view of anatomy.
- Some platforms provide 4K or near-4K resolution, enhancing visualization of planes, small vessels, and nerves.
- Dual-lens optics create depth perception that far surpasses standard 2D laparoscopy.
- Adjunct imaging (e.g., near-infrared fluorescence for perfusion or lymphatic mapping) can be integrated to guide intraoperative decisions.
Software and Integration Layer
- Real-time control software translates surgeon hand movements into instrument motion while filtering tremor.
- Safety algorithms prevent instrument collisions and restrict movement beyond defined boundaries.
- Preoperative imaging (CT, MRI) may be overlaid or referenced for planning and navigation in some advanced systems.
- Data capture and analytics can be used for quality improvement, skills assessment, and research.
Clinical Applications: Where Robotic Surgery Is Making the Biggest Impact
Robotic platforms are increasingly used across multiple specialties, especially where fine dissection, suturing, and complex reconstruction are required in confined spaces. Below are key domains where Robotic Surgery and Minimally Invasive Techniques have become standard or rapidly growing.
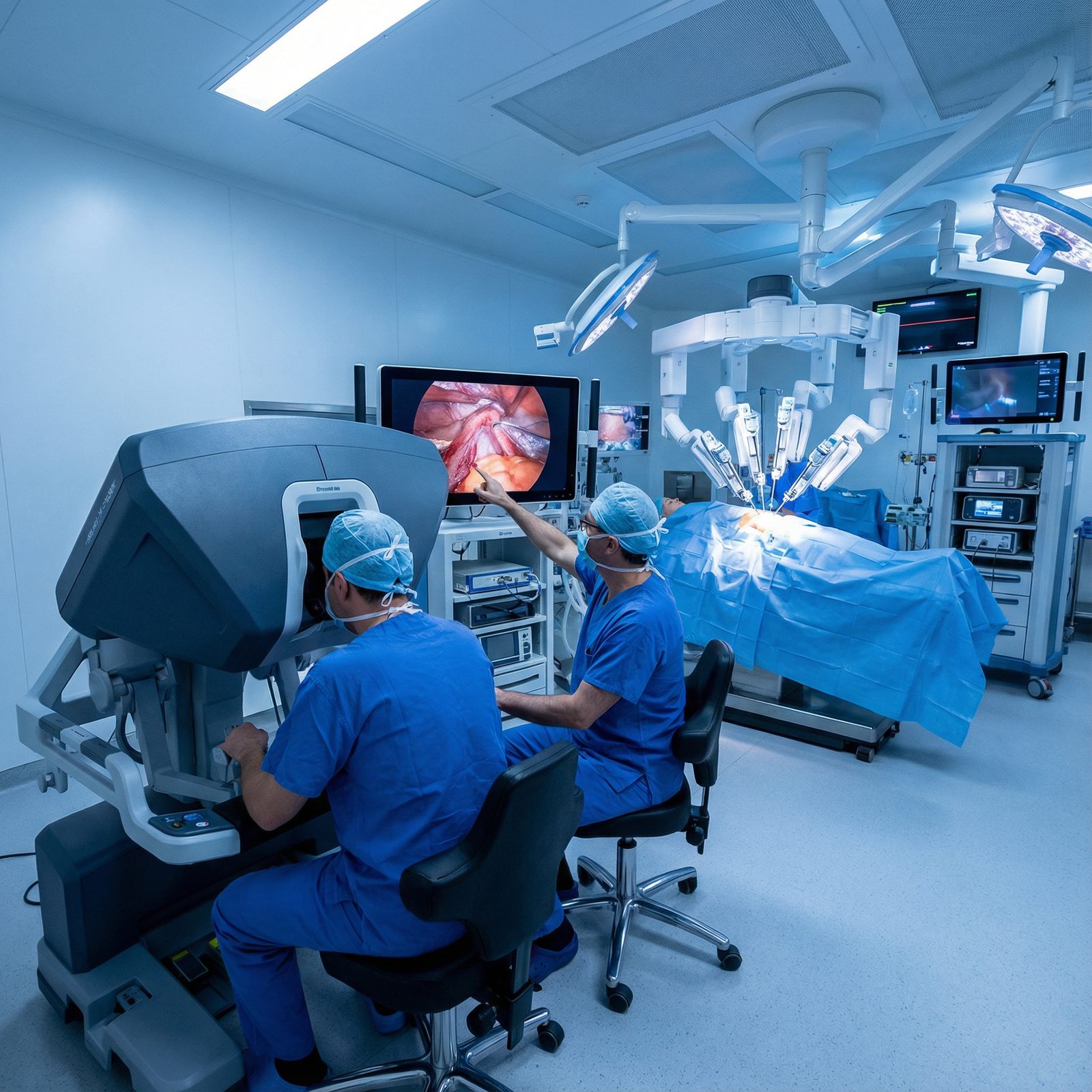
Urologic Surgery
Urology was one of the earliest adopters and remains one of the highest-volume users of robotic systems.
Radical Prostatectomy
Robotic-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy (RALP) is now the predominant approach in many regions. Evidence shows:- Reduced blood loss and transfusion rates compared with open surgery.
- Shorter length of stay and quicker return to continence in many series.
- Comparable or improved oncologic control when performed by experienced surgeons.
- Better nerve-sparing precision, often translating into improved erectile function recovery.
Partial Nephrectomy and Pyeloplasty
Robotic platforms are used for nephron-sparing kidney surgery and complex reconstruction:- Facilitates intracorporeal suturing in challenging angles.
- May reduce warm ischemia time due to efficient reconstruction.
- Enables minimally invasive treatment for larger or complex renal masses.
Gynecologic Surgery
Robotic systems are widely used in both benign and oncologic gynecology.
Hysterectomy and Myomectomy
- Enhanced dexterity helps with dense adhesions, large uteri, or complex myoma enucleation.
- Patients typically experience shorter hospital stay, less postoperative pain, and faster return to work.
- For obese patients or those with prior surgery, robotic access can significantly reduce the need for open abdominal procedures.
Gynecologic Oncology
- Used in staging procedures for endometrial and cervical cancers.
- May reduce wound complications and length of stay, important in patients who will proceed to adjuvant therapy.
Cardiac and Thoracic Surgery
Intrathoracic procedures benefit from enhanced visualization in tight spaces.
Mitral Valve Repair and Coronary Procedures
- Robotic-assisted mitral valve surgery allows repair via small thoracotomy incisions instead of full sternotomy.
- Lower rates of postoperative atrial fibrillation and shorter ICU and hospital stays are reported in some studies.
- A subset of coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) procedures can be performed robotically, particularly internal mammary artery harvesting.
Thoracic Oncology
- Lobectomies and mediastinal mass resections are increasingly performed robotically.
- Improved visualization of hilar and mediastinal structures supports meticulous lymph node dissection.
Head and Neck / Otorhinolaryngology
Transoral robotic surgery (TORS) has opened new possibilities in this field.
- Oropharyngeal and Laryngeal Tumors
- Allows access via the mouth without mandibulotomy or extensive open incisions.
- Can preserve speech and swallowing function better in selected patients.
- Often reduces tracheostomy and feeding tube dependence when combined with careful patient selection.
General, Colorectal, and Bariatric Surgery
Robotic platforms are rapidly expanding in general surgery, especially in complex minimally invasive cases.
Colorectal Surgery
- Rectal cancer resections in narrow pelvises benefit from enhanced dexterity and stable retraction.
- May reduce conversion rates to open surgery compared with conventional laparoscopy in technically challenging cases.
Hernia and Bariatric Procedures
- Complex ventral and hiatal hernia repairs are increasingly performed using robotic techniques.
- Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and other revisional bariatric procedures often leverage robotic precision for intricate anastomoses.
Benefits of Robotic Surgery: Precision, Visualization, and Better Patient Outcomes
From an outcomes standpoint, Robotic Surgery offers a combination of improved Surgical Precision, superior visualization, and a consistent platform for Minimally Invasive Techniques. For many indications, this translates into clinically meaningful benefits for patients and practical advantages for surgeons.
Enhanced Surgical Precision and Dexterity
Robotic systems are designed to exceed the mechanical limitations of the human hand.
Tremor Filtration
Natural physiologic tremor is filtered out, creating extremely stable instrument tips—especially important for microdissection near nerves and vessels.Motion Scaling
Hand movements can be downscaled (e.g., 3:1, 5:1), enabling tiny, controlled actions. This is particularly beneficial for suturing delicate structures, such as urethrovesical anastomoses, mitral leaflets, or bowel anastomoses.Wristed Instruments
Seven degrees of freedom and “endo-wristed” tools allow curved suturing angles that are difficult or impossible with straight laparoscopic instruments.
Collectively, these features support more meticulous dissection, precise hemostasis, and fine reconstruction, which can directly influence Patient Outcomes such as continence, sexual function, and organ preservation.
Superior Visualization of the Surgical Field
Visualization is a defining strength of robotic platforms.
3D, High-Definition Imaging
Depth perception allows surgeons to distinguish planes and identify tiny structures like lymphatic channels or microvessels.
Magnification (up to 10x) reveals tissue layers that are invisible to the naked eye.Adjunct Imaging Technologies
- Near-infrared fluorescence imaging (e.g., indocyanine green) enables real-time assessment of perfusion and identification of bile ducts, ureters, or lymph nodes.
- Integration of preoperative CT or MRI can guide dissection around tumors, vessels, or complex anatomy in some advanced systems.
Improved visualization not only supports better immediate technical outcomes but also reduces inadvertent injury to critical structures.
Minimally Invasive Techniques and Recovery Advantages
Robotic surgery is a platform for Minimally Invasive Techniques that can achieve outcomes equivalent or superior to open surgery, with less physiologic impact on patients.
Commonly observed benefits include:
Smaller Incisions, Less Pain
8–12 mm trocar sites replace long laparotomy or sternotomy incisions.
Reduced postoperative pain often allows earlier mobilization and decreased opioid requirements.Shorter Hospital Stay and Faster Recovery
Many robotic procedures can be performed as same-day or overnight stays.
Patients frequently return to work and baseline activity more quickly, which is economically and socially significant.Reduced Wound Complications
Smaller incisions translate into lower rates of wound infection, dehiscence, and incisional hernia in many patient populations.
Lower Complication Rates in Select Procedures
While outcomes vary by institution, surgeon experience, and case complexity, several trends are recurrent in the literature:
- Decreased blood loss and transfusion rates.
- Lower rates of wound infections and certain postoperative complications.
- In some settings, lower conversion rates to open surgery compared with standard laparoscopy.
For trainees and new attendings, it is crucial to interpret these benefits in context: robotic systems are tools. Their advantage depends heavily on appropriate case selection, structured training, and adherence to evidence-based perioperative care pathways.
Evidence in Practice: Illustrative Case Studies and Outcome Data
Multiple specialties have produced robust comparative studies analyzing the impact of Robotic Surgery on Patient Outcomes.
1. Robotic Prostatectomy: Functional and Oncologic Outcomes
A large comparative analysis in The Journal of Urology of men undergoing robotic-assisted versus open radical prostatectomy demonstrated:
Intraoperative Benefits
- Significantly less blood loss and lower transfusion rates.
- Reduced need for large abdominal incisions.
Postoperative Outcomes
- Shorter length of stay and quicker catheter removal in many cohorts.
- Improved early recovery of continence and erectile function in high-volume centers.
- Comparable or better positive margin rates and biochemical recurrence-free survival.
For urology residents and fellows, this has translated into a near-universal expectation of robotic proficiency in many markets.
2. Robotic Hysterectomy: Recovery and Patient Satisfaction
A 2019 study in Surgical Endoscopy compared robotic hysterectomy with traditional vaginal and open abdominal approaches:
- Robotic patients experienced:
- Shorter hospital stays and quicker return to full activity.
- Lower postoperative pain scores, particularly in the early postoperative period.
- High satisfaction rates regarding cosmetic outcomes and recovery.
In complex or obese patients where vaginal or conventional laparoscopic hysterectomy is challenging, robotics offers a viable minimally invasive alternative with comparable or improved safety.
3. Robotic Cardiac Surgery: High-Stakes Precision
A landmark study in The Annals of Thoracic Surgery evaluated robotic-assisted mitral valve repair versus conventional sternotomy:
- Patients undergoing robotic repair showed:
- Lower incidence of postoperative atrial fibrillation in some series.
- Reduced ICU and overall hospital length of stay.
- Faster return to baseline functional status.
These results are particularly compelling given the high physiologic stress of traditional cardiac surgery and the potential morbidity of sternotomy.
The Future of Robotic Surgery and Healthcare Technology: AI, AR, and Remote Operations
Robotic Surgery sits at the intersection of Medicine and Healthcare Technology, and the next decade will likely bring major shifts in how operations are planned, executed, and analyzed.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Automation
AI is beginning to influence every phase of surgery:
Preoperative Planning
- Automated segmentation of CT and MRI to map critical structures.
- Risk prediction models to help select optimal approaches (open vs laparoscopic vs robotic).
Intraoperative Guidance
- Real-time recognition of anatomy and critical zones.
- AI-based alerts if instruments approach high-risk structures.
- Context-aware assistance, such as suggested next steps or recommended instrument changes.
Training and Assessment
- Objective performance metrics (economy of motion, instrument path, suture placement) derived from console data.
- Automated scoring systems for resident and fellow skills, enabling competency-based progression rather than case-count alone.
Full autonomy is not the near-term goal; instead, AI will act as a “co-pilot” enhancing Surgical Precision and safety.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Image-Guided Surgery
AR overlays can superimpose preoperative imaging on the live surgical field:
- Highlight tumor margins, vascular structures, or nerves.
- Display real-time perfusion maps.
- Provide step-by-step guidance in standardized procedures or rare anatomic variants.
These tools are especially promising in neurosurgery, hepatobiliary, and complex oncologic resections.
Remote Surgery and Telestration
The concept of remote robotic surgery—where the surgeon is physically distant from the patient—has already been demonstrated technically.
Tele-mentoring and Telestration
- Senior surgeons can annotate live video, guide dissection planes, and advise less experienced colleagues across institutions or countries.
- This is already affecting global access to advanced Minimally Invasive Techniques.
True Remote Operations
- Wider adoption will require ultra-low latency networks (e.g., 5G and beyond), standardized platforms, robust cybersecurity, and clear regulation.
- Remote surgery could help address geographic disparities in surgical subspecialty access.
For residents and new attendings, these trends mean that comfort with digital tools, data, and networked systems will be an important complement to operative skill.
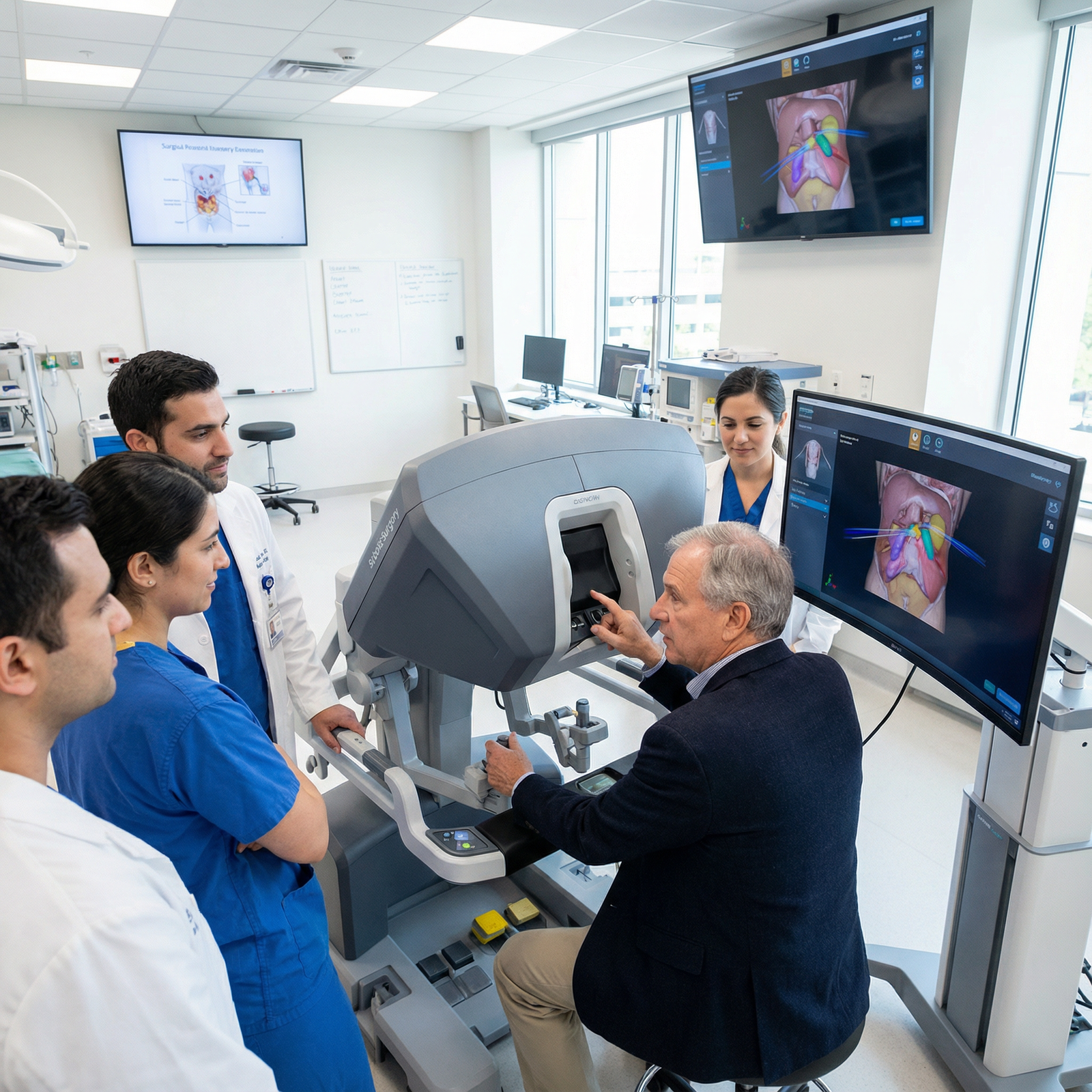
Training, Credentialing, and Career Impact in the Post-Residency Era
For surgeons entering the job market, robotic proficiency can be a competitive differentiator, especially in urology, gynecology, general surgery, and cardiothoracic fields.
Training Pathways
Residency and Fellowship Exposure
- Simulator-based curricula (virtual reality consoles) for fundamental skills.
- Stepwise participation: bedside assisting → console time in low-complexity cases → primary console surgeon under supervision.
- Objective proficiency metrics increasingly used for sign-off.
Industry and Society Courses
- Formal multi-day courses combining didactics, dry labs, and cadaver labs.
- Proctoring programs for new faculty to safely build case volume.
Credentialing and Hospital Requirements
Most institutions have defined requirements for robotic privileges:
- Minimum number of proctored cases.
- Evidence of simulator or lab-based training.
- Ongoing volume thresholds to maintain competency.
Early-career surgeons should plan their training trajectory with these requirements in mind, documenting cases and training experiences carefully.
Strategic Considerations for Job Seekers
- Understand local market saturation of robotic platforms and case volumes.
- Clarify access to console time, competition with senior partners, and support for new program development.
- Explore opportunities to participate in research, quality improvement, or innovation projects related to Robotic Surgery and Healthcare Technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What types of surgeries are most commonly performed using Robotic Surgery?
Robotic Surgery is frequently used in:
- Urology: Radical prostatectomy, partial nephrectomy, pyeloplasty.
- Gynecology: Hysterectomy, myomectomy, endometrial cancer staging.
- General and Colorectal Surgery: Colectomies, rectal cancer resections, hernia repairs, bariatric procedures.
- Cardiothoracic Surgery: Mitral valve repair, selected coronary procedures, lobectomy.
- Head and Neck: Transoral robotic surgery for oropharyngeal tumors.
The list continues to expand as systems and techniques evolve, particularly for complex Minimally Invasive Techniques that demand high Surgical Precision.
2. Are robotic surgeries safer than traditional open procedures?
Robotic surgery is generally at least as safe as traditional approaches when performed by trained surgeons, and in many contexts it offers measurable advantages:
- Less blood loss and lower transfusion rates in numerous procedures.
- Smaller incisions with fewer wound complications.
- Shorter hospitalization and faster return to normal activity.
However, safety and outcomes depend heavily on surgeon experience, appropriate patient selection, and institutional support. Robotic platforms are tools—poorly selected cases or inadequate training can negate their potential benefits.
3. How does robotic surgery differ from standard laparoscopy?
Both are minimally invasive, but key differences include:
- Visualization: Robotic systems provide 3D high-definition vision versus the 2D view of standard laparoscopy.
- Dexterity: Wristed instruments with more degrees of freedom versus straight laparoscopic tools.
- Ergonomics and Control: Surgeons operate from a console, often more ergonomically, with motion scaling and tremor filtration.
Standard laparoscopy remains ideal for many straightforward cases. Robotics becomes particularly advantageous in complex reconstructions, deep pelvic dissection, or operations in narrow anatomic spaces.
4. Who actually performs the surgery when a robot is used?
The surgeon performs the surgery. The robot does not act autonomously:
- The surgeon sits at the console and directly controls all instrument movements.
- A bedside assistant manages suction, retraction, stapling, and instrument exchanges.
- Anesthesia, nursing, and technical staff support the procedure as in any major operation.
Robotic systems are best viewed as advanced, computer-enhanced instrument platforms under full human control.
5. Is Robotic Surgery more expensive, and how is that justified?
Robotic systems involve substantial capital costs, maintenance fees, and instrument expenses. However, several factors may offset these costs:
- Shorter hospital stays and fewer postoperative complications.
- Faster return to work and daily function for patients.
- Potential institutional benefits from improved Patient Outcomes and market competitiveness.
Cost-effectiveness varies by procedure type, case volume, and health system structure. For early-career surgeons, understanding local payer dynamics and institutional priorities is crucial when planning robotic program development or expansion.
By combining advanced Healthcare Technology, refined Minimally Invasive Techniques, and data-driven training, Robotic Surgery is reshaping what is possible in the operating room. For trainees and new attendings, developing competence and critical judgment in this domain is now a core element of modern surgical practice and a key asset in the post-residency job market.




















