
Choosing General Surgery as a career means committing to a demanding, high‑stakes specialty that requires stamina, precision, and lifelong learning. Because of the intensity and prestige of Surgery Training, the General Surgery Residency Application process is highly competitive and often confusing—especially if you are the first in your school or family to pursue it.
This guide walks you step‑by‑step through the process, from early preparation in medical school to the Match, with practical Interview Tips, examples, and strategies you can use right away. The goal is to help you apply strategically and confidently, while also assessing whether a given program is the right fit for you.
Understanding General Surgery Residency and What Programs Look For
Before dissecting the application process itself, it’s crucial to understand what General Surgery training involves and what residency program directors value in an applicant.
What a General Surgery Residency Entails
General Surgery residency in the United States is typically 5 clinical years. Some programs include a mandatory or optional 1–2-year research block, stretching training to 6–7 years.
During residency, you will:
- Rotate through core services such as:
- General/acute care surgery
- Trauma and critical care
- Colorectal surgery
- Surgical oncology
- Vascular surgery
- Minimally invasive surgery
- Gain experience in:
- Preoperative evaluation and risk assessment
- Intraoperative technical skills (from suturing to complex open and laparoscopic procedures)
- Postoperative management and complications
- ICU care and trauma resuscitation
- Develop key non-technical skills:
- Communication with patients, families, and multidisciplinary teams
- Leadership and “running the list” on busy services
- Time management and prioritization
- Resilience and coping strategies for a demanding lifestyle
Residency is physically and emotionally intensive. Long hours, overnight call, and high-acuity patients are the norm. Programs therefore look for applicants who not only have strong academic metrics but also demonstrate reliability, work ethic, maturity, and a realistic understanding of the field.
What General Surgery Programs Value in Applicants
While each program is unique, most General Surgery residency selection committees focus on:
- Clinical performance
- Honors/High Pass in core clerkships, especially Surgery and Medicine
- Sub-internship (Sub-I) or Acting Internship evaluations in surgery
- Standardized exams
- USMLE/COMLEX Step 2 CK is increasingly important
- Step 1 (if numeric) still matters but is less decisive than before
- Surgical exposure and commitment
- Demonstrated sustained interest in surgery (electives, sub-Is, student surgical societies)
- Strong letters of recommendation from surgeons who know you well
- Professionalism and teamwork
- Narrative comments in MSPE (Dean’s letter)
- Feedback about your behavior on teams, reliability, and humility
- Scholarly activity
- Research in surgery or related fields, especially with publications or presentations
- Personal qualities
- Grit, teachability, curiosity, empathy, and leadership potential
- A story and career goals that make sense for surgery
Understanding these expectations will help you plan your activities, highlight your strengths, and address weaknesses proactively.
Phase 1: Early Preparation Before Your Application Year
Your “application” to General Surgery doesn’t start when ERAS opens—it begins the moment you start medical school. Smart, early planning can dramatically improve your competitiveness and reduce stress later.
Build a Strong Academic Foundation
- Aim for solid preclinical performance. While preclinical grades are not everything, consistent effort sets habits that pay off during clinical years.
- Take foundational sciences seriously. A strong understanding of anatomy, physiology, and pathophysiology will make surgery clerkships and Step 2 CK easier.
- Plan ahead for standardized exams.
- Step 1 (if you still receive a numerical score): aim for at least the national average for surgery applicants or higher.
- Step 2 CK: increasing importance; programs may use this as a screening tool.
If your scores are lower than you hoped:
- Focus on maximizing clinical grades and narrative comments.
- Strengthen other components like research, letters, and interview performance.
- Consider a more balanced or broader application strategy.
Engage in Surgical Research and Scholarly Work
Research is not mandatory for every General Surgery residency, but it helps you:
- Demonstrate commitment to academic medicine and critical thinking.
- Build strong relationships with surgical mentors.
- Create talking points for interviews.
Actionable steps:
- Join a surgical lab or clinical outcomes research group early (MS1 or MS2 if possible).
- Start with manageable tasks:
- Chart reviews
- Case reports or case series
- Retrospective database studies
- Aim for:
- At least one abstract, poster, or oral presentation.
- A manuscript submission (even if it’s still under review at application time).
Prioritize quality and depth of involvement over sheer quantity of projects.
Maximize Surgical Exposure and Mentorship
Programs want to know: Do you understand what life as a surgeon is really like?
Ways to build authentic exposure:
- Shadow in the OR and clinic. Observe attendings and residents to understand workflow, culture, and expectations.
- Join your school’s surgery interest group. Attend talks, skills workshops, and panel discussions.
- Pursue elective rotations in surgery:
- Early elective: confirm your interest and start networking.
- Late MS3/MS4: develop relationships for letters and gain advanced skills.
Mentorship tips:
- Identify 1–2 attendings and at least one senior resident or fellow as mentors.
- Meet periodically to:
- Discuss your goals and progress.
- Ask for honest feedback.
- Plan rotations, research, and your Residency Application strategy.
These mentors can later become powerful advocates in your letters of recommendation and networking efforts.
Phase 2: Crafting a Competitive ERAS Application
The Electronic Residency Application Service (ERAS) is where your entire story comes together—academics, experiences, and narrative. Treat it like a professional portfolio, not just a form to complete.
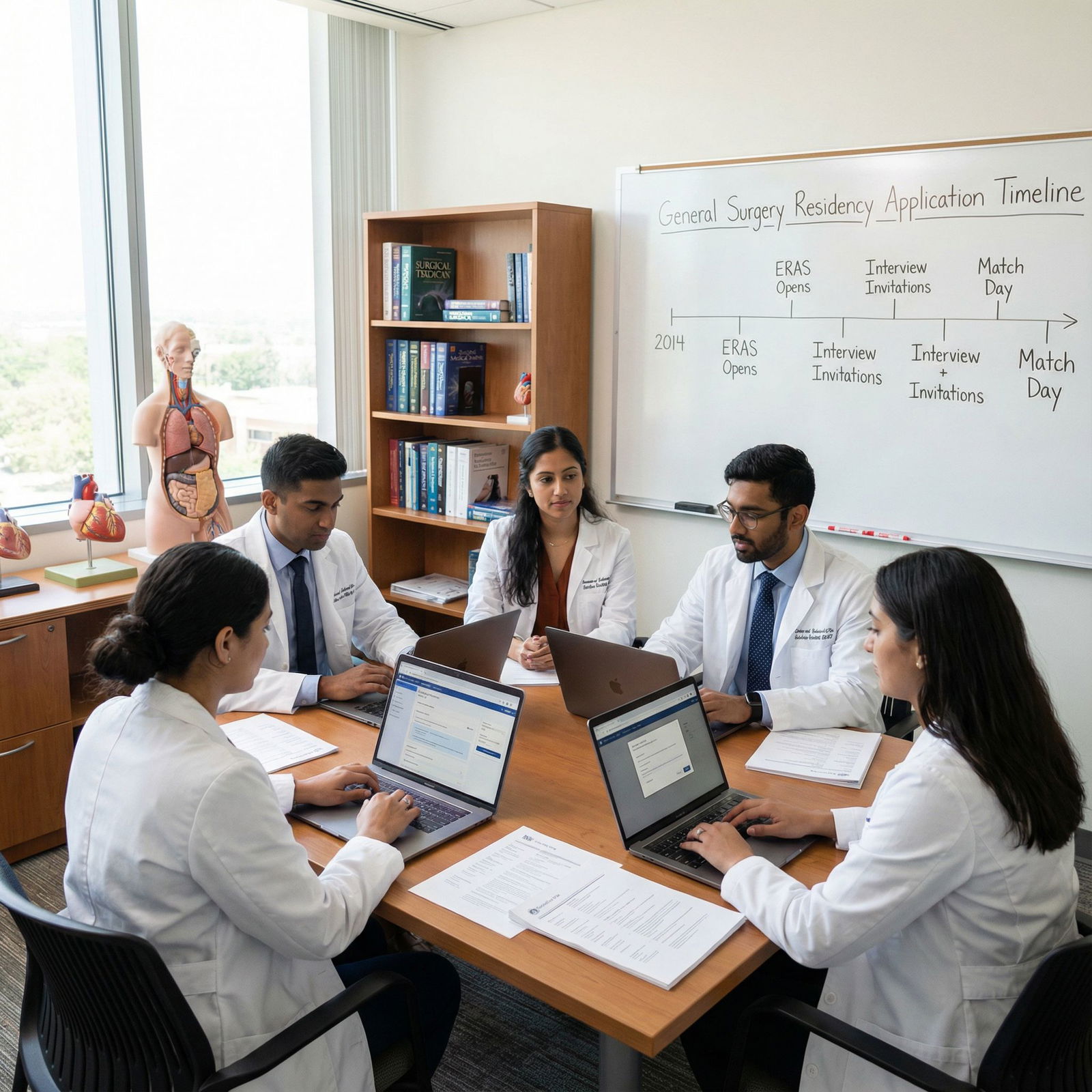
Know the ERAS Timeline and Key Deadlines
While exact dates vary year-to-year, the typical timeline is:
- June – ERAS opens for applicants; you can start entering information.
- Late summer (August–September) – Programs can begin to view applications shortly after submission opens.
- September – Aim to have:
- Personal statement finalized
- Letters of recommendation uploaded
- USMLE/COMLEX scores available (at least Step 1 and often Step 2 CK)
- October–January – General Surgery interview season.
- February – Rank Order List due for NRMP Match.
- March – Match Week and Match Day.
Build in time for:
- Multiple drafts and feedback on your personal statement.
- Giving letter writers at least 4–6 weeks to write.
- Receiving and uploading transcripts and MSPE.
Writing a Powerful Surgery Personal Statement
Your personal statement is not a diary entry; it’s a focused, professional narrative explaining:
- Why General Surgery is the right specialty for you.
- What experiences shaped your interest and suitability.
- What you bring to a program (skills, values, goals).
- How you envision your future in surgery (academic, community, global, subspecialty interests, etc.).
Tips for an effective statement:
- Open with a specific, meaningful story, not a generic quote.
- Example: a night on trauma call that changed your view of teamwork and responsibility.
- Connect your experiences to core surgical values:
- Ownership, precision, resilience, advocacy for patients.
- Show insight and humility. Discuss challenges you’ve faced and what you learned.
- Avoid clichés like “I like to work with my hands” without deeper explanation.
- Keep it concise and readable (usually 1 page, 600–800 words).
Have at least one surgeon and one trusted advisor or mentor review it for content and tone.
Letters of Recommendation: Quality Over Quantity
For General Surgery, strong letters can significantly elevate your application.
Who to ask:
- At least 2–3 letters from surgeons (academic or community).
- Ideally, one from your Surgery clerkship or sub‑I director.
- Others from attendings you worked with closely on clinical services or research.
- An additional letter (optional) from:
- A non-surgical faculty member (Medicine, ICU, etc.) who can speak to your clinical excellence and teamwork.
- A research mentor (especially if your research is substantial).
How to secure strong letters:
- Ask in person when possible, and ask explicitly:
“Do you feel you can write me a strong letter of recommendation for General Surgery?” - Provide:
- Your updated CV
- Draft of personal statement
- Brief summary of your work with them
- Your future goals (academic vs. community, interest areas)
- Request letters early—at least 4–6 weeks before deadlines.
- Use the ERAS letter portal instructions precisely.
Presenting Your Experiences and CV Effectively
When filling out ERAS:
- Be accurate and honest. Do not inflate roles or outcomes.
- Highlight leadership roles (e.g., surgery interest group, quality improvement committees).
- Detail meaningful experiences:
- A short description of impact: what you did, what you learned, and outcomes (e.g., process improved, abstract accepted).
- Group similar experiences (e.g., multiple community surgery outreach events) to avoid clutter.
- Select “Most Meaningful” experiences wisely, focusing on depth and transformation rather than sheer prestige.
Phase 3: The General Surgery Interview Season
Once programs review Residency Applications, they extend interview invitations, often starting in October. Because interviews are the main way programs assess your personality, communication, and fit, they can strongly influence your rank position.
Preparing for Surgery Residency Interviews
Key preparation steps:
- Know your application inside out.
- Be ready to discuss any research project, activity, or grade.
- Re‑read your personal statement and CV before each interview.
- Practice common questions.
- “Why General Surgery?”
- “Why this program?”
- “Tell me about a complication or mistake and how you handled it.”
- “Describe a conflict on the team and your role.”
- “What are your career goals (fellowship, academic vs. community)?”
- Develop your own talking points.
- 3–4 key strengths you want interviewers to remember.
- 1–2 challenges you’ve overcome and what they taught you.
- Mock interviews.
- Use your school’s career office, faculty mentors, or peers.
- Practice both traditional and behavioral questions using the STAR method (Situation, Task, Action, Result).
Virtual interview tips (increasingly common):
- Test your technology, camera, microphone, and background.
- Dress in full professional attire (not just the top half).
- Maintain eye contact by looking at the camera, not the screen.
- Minimize distractions and background noise.
Presenting Yourself Professionally
Whether in-person or virtual:
- Dress code: Conservative business attire.
- Suit and tie, or professional blouse/jacket and slacks or skirt.
- Neutral colors are safest; aim to look polished, not flashy.
- Body language:
- Firm (but not crushing) handshake in person.
- Sit upright, open posture, attentive listening.
- Communication style:
- Answer clearly and concisely.
- Avoid overly negative talk about other institutions or individuals.
- Show genuine curiosity: ask thoughtful questions about training, mentorship, and resident experience.
Following Up After Interviews
While thank‑you notes rarely determine your rank, they are considered professional and can reinforce a positive impression.
Good practices:
- Send a brief, personalized email to each interviewer within 24–72 hours.
- Mention a specific topic you discussed or something you appreciated about the conversation.
- Reaffirm your interest in the program (without making disingenuous promises).
- Keep messages short and sincere; avoid generic templates across all programs.
Phase 4: Navigating the NRMP Match for General Surgery
The National Resident Matching Program (NRMP) coordinates how applicants and programs pair up. Understanding the Match process will help you strategize your rank list.
Creating a Thoughtful Rank Order List
After interviews (usually January–February), you’ll rank programs based on preference. Some considerations:
- Training quality and case volume
- How early do residents get into the OR?
- Operative autonomy for chief residents?
- Breadth of cases: trauma, minimally invasive, complex cancer cases, etc.
- Program culture and resident morale
- Were residents candid and satisfied?
- How do they describe workload, support, and feedback culture?
- Location and lifestyle
- Proximity to family/support network.
- Cost of living and commute.
- Opportunities for partner/children, if applicable.
- Academic opportunities
- Research infrastructure and protected time.
- Fellowship match track record (e.g., surgical oncology, vascular, colorectal, MIS).
- Program structure
- Traditional 5-year vs. 5+2 research tracks.
- Presence of prelims and how they are integrated.
Important: Always rank programs in your true order of preference, not how you think programs will rank you. The NRMP algorithm is applicant-favoring—your honest preferences matter.
Understanding the Match Algorithm in Simple Terms
The NRMP algorithm:
- Starts with the applicant’s first choice.
- Checks if the program has ranked the applicant and has available spots.
- If yes, tentatively places the applicant there.
- If not, moves to the applicant’s next choice.
- The algorithm iteratively adjusts placements to optimize applicants’ highest possible choices within programs’ ranked preferences.
Implications for you:
- Do not try to “game” the system by ranking “safety” programs higher than you actually prefer.
- It is better to have a well-balanced but honest list, including:
- A mix of highly competitive, mid-range, and safer programs.
- Enough total programs to statistically improve your chance of matching.
Evaluating and Choosing General Surgery Programs Wisely
Not all General Surgery residencies are the same. Thoughtful program selection can profoundly impact your training experience and career trajectory.
Key Program Features to Research
When building your initial application list and refining it post-interview, examine:
- Curriculum and rotation structure
- Distribution of rotations by PGY year.
- Early exposure to operative cases vs. predominantly floor/ICU work.
- Case volume and complexity
- ACGME case logs and resident reports.
- Operative autonomy policy and culture.
- Resident support and wellness
- Duty hour compliance.
- Access to mental health resources, mentoring systems, and wellness initiatives.
- Evaluation and feedback
- Frequency of formal feedback and milestones review.
- Opportunities for remediation and support if struggling.
- Diversity, equity, and inclusion efforts
- Representation among residents and faculty.
- Formal DEI initiatives and mentoring for underrepresented groups.
Considering Fellowship and Career Outcomes
If you’re interested in a subspecialty (e.g., surgical oncology, vascular, colorectal, trauma/critical care):
- Review the program’s fellowship match record over the last 5–10 years.
- Ask:
- How many graduates go into fellowship vs. general practice?
- In which institutions and subspecialties have recent graduates matched?
- Look for:
- Access to subspecialty services and faculty.
- Support for research and national networking (e.g., sending residents to conferences).
Resilience, Wellness, and Preparing for the Demands of Surgery Training
The General Surgery path is rewarding but demanding. Your wellbeing during the application process and residency itself is not optional—it’s foundational to safe, sustainable practice.
Maintaining Perspective During a Stressful Application Cycle
You may encounter setbacks:
- Fewer interviews than expected.
- Rejections from programs you liked.
- Anxiety comparing yourself to classmates.
To stay grounded:
- Remember that rejections do not define your worth or future as a surgeon.
- Focus on what you can control: preparation, professionalism, and attitude.
- Lean on support systems:
- Friends, family, mentors, mental health professionals.
- Peer groups going through the same process.
If your initial cycle does not go as hoped:
- Consider a strategic plan:
- Research years, prelim positions, or broadening specialty options.
- Honest conversations with advisors about competitiveness and next steps.
- Many successful surgeons took non-linear paths—your trajectory can still be strong.
Protecting Your Mental and Physical Health
Practical steps during medical school and residency:
Physical health
- Regular exercise, even short walks or quick workouts.
- Prioritizing sleep when possible; avoiding unnecessary all-nighters.
- Healthy(ish) eating habits amidst hospital schedules.
Emotional resilience
- Mindfulness, meditation, or other stress-management techniques.
- Setting boundaries and saying “no” when overloaded.
- Seeking counseling or therapy early if experiencing burnout, anxiety, or depression.
Professional sustainability
- Developing efficient study habits.
- Learning to ask for help and delegate on teams.
- Reflecting periodically on your goals and adjusting when needed.
Conclusion: Owning Your Path to a General Surgery Residency
Applying to General Surgery residencies is challenging, but with deliberate planning and self-awareness, you can navigate it successfully.
Key takeaways:
- Start early with strong academics, surgical exposure, and mentorship.
- Build a cohesive application through ERAS that reflects authentic commitment to surgery.
- Prepare thoughtfully for interviews and present yourself as a capable, teachable future colleague.
- Use the NRMP Match process to prioritize your true preferences while being realistic and strategic.
- Evaluate programs beyond name recognition—focus on culture, training quality, wellness, and fit.
- Protect your mental and physical health through this demanding but rewarding process.
Your Residency Application tells the story of who you are and the surgeon you aspire to become. Every grade, letter, and interview is a piece of that narrative—but none of them alone defines you. Stay curious, stay humble, and seek out environments where you will be challenged, supported, and inspired to grow into the surgeon your patients deserve.
Frequently Asked Questions About General Surgery Residency Applications
1. How important is research experience for getting into a General Surgery residency?
Research is increasingly valued, especially at academic programs, but it is not an absolute requirement for every applicant or every program. Having surgical or clinically relevant research with posters, presentations, or publications:
- Shows commitment to academic inquiry and evidence-based practice.
- Helps you build relationships with faculty who can write strong letters.
- Provides excellent material for interview discussions.
If you don’t have extensive research, you can still be competitive by emphasizing strong clinical performance, excellent letters, and clear commitment to surgery. For highly academic or research-focused programs, however, research experience is a significant advantage.
2. What is the typical timeline for applying to General Surgery residencies?
The core timeline in your final year of medical school usually looks like this:
- Spring (MS3/MS4 transition): Decide on specialty, finalize sub-I plans, and identify letter writers.
- Summer: Complete sub-Is, refine CV, draft personal statement, and request letters.
- June–September: ERAS opens; you enter data, finalize documents, and submit your application when allowed.
- October–January: Interview season for General Surgery.
- February: Submit your NRMP Rank Order List.
- March: Match Week and Match Day.
Plan backward from these dates to ensure you have research, clerkship evaluations, and letters ready in time.
3. How does the NRMP Match process work for General Surgery?
For General Surgery, the National Resident Matching Program uses the same algorithm as other specialties:
- You and programs each create rank order lists.
- The algorithm attempts to place you into your highest-ranked program that also ranks you and has available slots.
- If your top choice cannot take you, the algorithm considers your next choice, and so on.
Because the system is applicant-favoring, you should always rank programs in your true order of preference, not based on where you think you are more likely to match. A well-balanced list with an adequate number of programs is key to maximizing your chances.
4. What can I do to strengthen my application if I have lower board scores?
Lower USMLE/COMLEX scores are not the end of your General Surgery ambitions. You can mitigate them by:
- Excelling clinically: Aim for Honors/High Pass in Surgery and Medicine; obtain outstanding narrative comments.
- Securing exceptional letters: Choose letter writers who know you well and can speak to your strengths, work ethic, and growth.
- Highlighting unique strengths: Research, leadership, prior careers, language skills, or service experiences.
- Improving Step 2 CK performance: A stronger Step 2 CK score can partially offset a weaker Step 1.
- Applying strategically: Consider a broader list of programs, including community-based and mid-sized academic centers.
Advisors and mentors can help you calibrate expectations and form a realistic program list.
5. How many General Surgery programs should I apply to, and how do I build a balanced list?
Numbers vary by applicant profile and competitiveness of specific cycles, but many U.S. senior applicants to General Surgery apply to roughly 25–40 programs. Factors that influence how many you should apply to include:
- Academic metrics (Step scores, grades).
- Strength of letters and research.
- Geographic restrictions or preferences.
- Whether you are an international medical graduate (IMG) or DO graduate.
A balanced list typically includes:
- A handful of more competitive “reach” academic programs.
- A solid core of mid-range academic and strong community programs.
- Several “safety” programs where your metrics and profile are comfortably above their usual averages.
Discuss your specific situation with advisors or mentors who know the current General Surgery application landscape.
Thoughtful preparation and honest self-assessment, combined with clear guidance from mentors and resources, will help you navigate General Surgery residency applications with confidence and purpose.


















