
Alzheimer’s Disease remains one of the most challenging neurodegenerative disorders faced by modern medicine. For residency applicants and early-career clinicians, understanding the rapidly evolving landscape of Research Advancements and Treatment Innovations is essential—not only for patient care, but also for ethical decision-making, communication with families, and long-term career development in cognitive health.
Below is an expanded, clinically focused overview of current knowledge, emerging therapies, and the practical implications for future physicians.
Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease: Pathophysiology, Course, and Clinical Impact
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by cognitive decline, functional impairment, and behavioral changes. It is the leading cause of dementia worldwide and a major driver of morbidity, mortality, and healthcare utilization in aging populations.
Core Neuropathology
At the microscopic level, Alzheimer’s is defined by two hallmark lesions:
Amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques
- Extracellular deposits of misfolded amyloid-β peptides
- Thought to arise from abnormal cleavage of amyloid precursor protein (APP)
- Associated with synaptic dysfunction and neurotoxicity
Neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs)
- Intracellular aggregates of hyperphosphorylated tau protein
- Disrupt microtubule stability and axonal transport
- Correlate more closely with the severity of cognitive decline than plaques
The cumulative effect of these pathologic processes is synaptic loss, neuronal death, brain atrophy—particularly in the hippocampus and medial temporal lobes—and progressive impairment of memory, executive function, and ultimately basic activities of daily living.
Clinical Phenotypes and Progression
While the “classic” amnestic presentation remains most common, future clinicians should recognize that Alzheimer’s Disease presents along a spectrum:
Preclinical AD
- Pathology present, but no overt symptoms
- Biomarker-positive individuals with “normal” cognition
Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) due to AD
- Subjective and objective cognitive decline
- Preserved independence in daily activities
- High risk of progression to dementia
Alzheimer’s Dementia
- Cognitive impairment severe enough to affect independence
- Symptoms may include:
- Episodic memory loss
- Word-finding difficulty
- Impaired judgment and problem-solving
- Disorientation to time or place
- Neuropsychiatric symptoms (apathy, anxiety, depression, agitation)
Risk Factors: Beyond Age and Genetics
While age is the strongest risk factor, a nuanced understanding of modifiable and non-modifiable risks is crucial for counseling and prevention strategies:
Non-modifiable factors
- Advanced age
- Genetics (e.g., APOE ε4 allele; autosomal dominant mutations in APP, PSEN1, PSEN2 in familial AD)
- Family history of Alzheimer’s or other neurodegenerative disorders
- Female sex (in part due to longevity, but possibly hormonal and biologic factors as well)
Modifiable and lifestyle-related factors
- Vascular risk factors (hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, obesity)
- Smoking and excessive alcohol use
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Low educational attainment and limited cognitive engagement
- Social isolation
- Untreated hearing loss and sleep disorders (e.g., sleep apnea)
For trainees, this risk framework is the foundation for primary and secondary prevention counseling, and it underscores the intersection of neurology, psychiatry, internal medicine, and public health in cognitive health.
Recent Research Advancements in Alzheimer’s Disease
Advances in basic science, imaging, and translational research are reshaping how we approach Alzheimer’s—from a purely symptomatic model toward biologically defined, disease-modifying strategies.
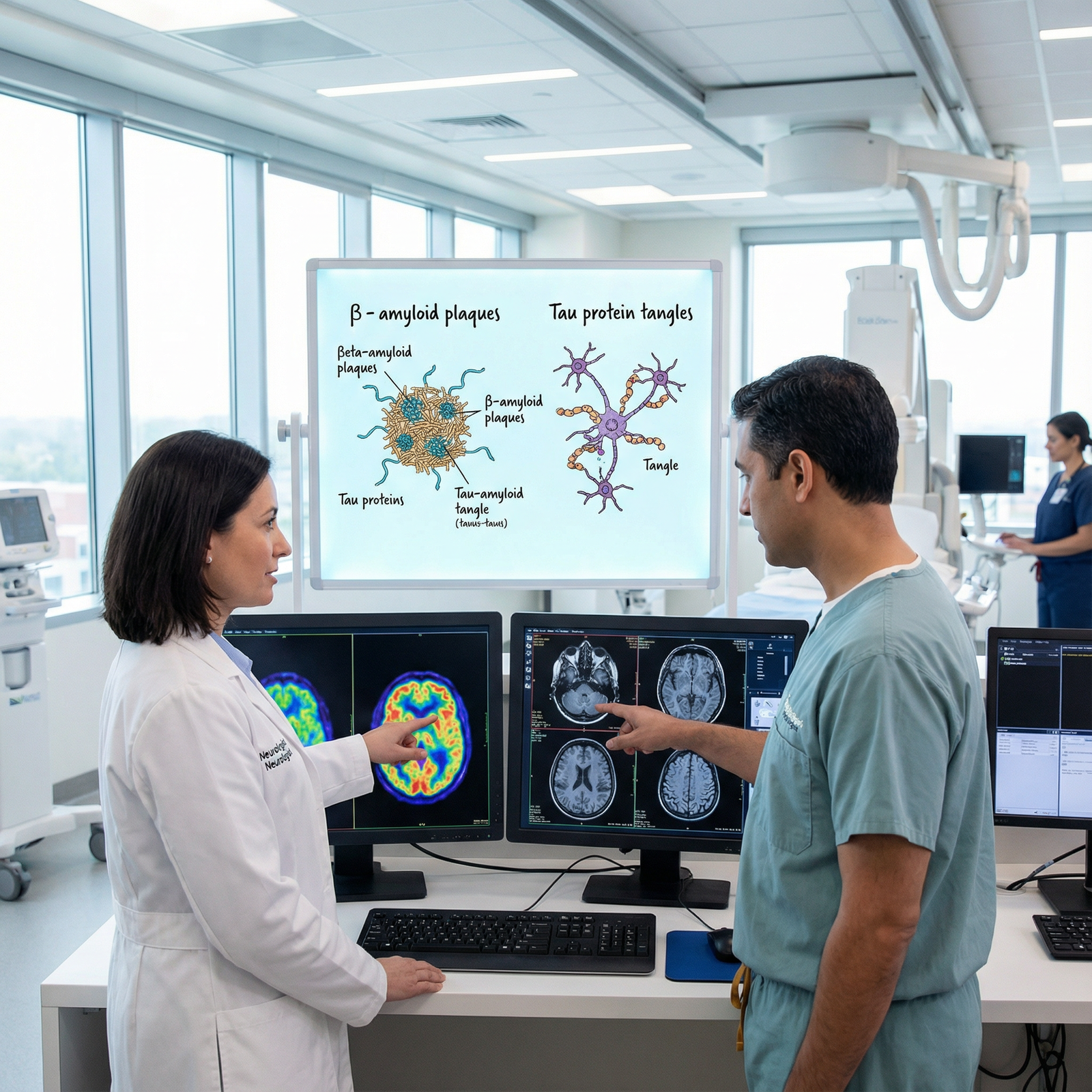
1. Biomarkers and Early Detection: Redefining Diagnosis
The field is moving from a “clinical-only” diagnosis toward a biomarker-based framework:
Imaging Biomarkers
Amyloid PET
- Uses radiolabeled tracers to visualize amyloid plaques in vivo
- Helpful in distinguishing Alzheimer’s pathology from other dementias
Tau PET
- Detects tau aggregates, providing insight into disease stage and severity
- Strongly associated with clinical symptoms and progression
Structural MRI
- Reveals hippocampal atrophy and global brain volume loss
- Useful for staging and ruling out other structural causes
Fluid Biomarkers
CSF biomarkers
- ↓ Aβ42 (or Aβ42/40 ratio)
- ↑ total tau and phosphorylated tau (p-tau)
- Help confirm underlying AD pathology
Blood-based biomarkers (rapidly emerging)
- Plasma p-tau217, p-tau181, and other markers are showing strong diagnostic performance
- Potential to transform screening and monitoring due to lower cost and easier access
Clinical implication: Early diagnosis enables enrollment in clinical trials, timely counseling, and potential initiation of disease-modifying therapies during stages when they are most likely to be effective.
2. Targeting Amyloid: Monoclonal Antibodies and Beyond
Amyloid-focused therapy has dominated Alzheimer’s research for decades. After many disappointments, several monoclonal antibodies have now shown the ability to reduce amyloid burden and modestly slow cognitive decline in selected patients.
- Lecanemab and donanemab (and previously aducanumab)
- Humanized monoclonal antibodies targeting aggregated Aβ
- Administered intravenously at regular intervals
- Clinical trials show:
- Robust reduction of amyloid plaques on PET
- Slowing of decline on cognitive and functional scales in early symptomatic patients
Key considerations for clinicians:
- Best suited for MCI due to AD or mild Alzheimer’s dementia with biomarker confirmation
- Require careful monitoring for amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA)—vasogenic edema or microhemorrhages detected on MRI
- Shared decision-making is ethically critical, as benefits are modest, risks are non-trivial, and costs are high
These therapies are among the first to move Alzheimer’s disease into the realm of disease modification rather than pure symptomatic treatment.
3. Tau-Targeted Therapies: Addressing the “Downstream” Driver
Given the strong correlation between tau pathology and clinical symptoms, there is intense interest in tau-directed interventions:
- Anti-tau monoclonal antibodies
- Aim to neutralize extracellular tau and prevent spread between neurons
- Tau aggregation inhibitors and kinase inhibitors
- Seek to reduce tau phosphorylation and aggregation
- Antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs)
- Designed to lower production of tau at the mRNA level
Many tau therapies remain in early or mid-phase clinical trials, but they represent a promising second wave of disease-modifying strategies that may be used in combination with amyloid therapies.
4. Neuroinflammation and Microglial Modulation
Neuroinflammation is now recognized as a central contributor to Alzheimer’s pathogenesis rather than a mere byproduct.
- Microglia, the brain’s resident immune cells, can:
- Clear amyloid and debris in their protective role
- Become chronically activated and secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines, exacerbating neuronal injury
Current research focuses on:
- Modulating microglial activation states
- Targeting pathways involving TREM2, a microglial receptor linked to AD risk
- Developing novel anti-inflammatory agents that are more targeted than traditional NSAIDs
Understanding this immune component opens an avenue for therapies that combine amyloid, tau, and inflammation modulation—a more holistic approach to neurodegenerative disorders.
5. Neuroprotective and Metabolic Strategies
Multiple agents and strategies aim to enhance neuronal resilience and synaptic function:
Natural compounds and nutraceuticals
- Curcumin, resveratrol, omega-3 fatty acids, and polyphenols are under investigation for antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties
- Current evidence is mixed; these are usually considered adjuncts rather than standalone treatments
Metabolic approaches
- Interest in intranasal insulin, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and ketone-based therapies reflects the overlap between AD and metabolic dysfunction
- Ongoing trials may clarify which agents truly modify disease vs. offer symptomatic benefits
Neurotrophic and synaptic-focused therapies
- Agents targeting BDNF pathways and synaptic plasticity are being explored to support neural circuits even in the presence of pathology
6. Gene Therapy and Precision Medicine
Gene-based approaches, while early-stage, are transforming the long-term horizon:
CRISPR and gene editing
- Potential to correct high-penetrance mutations in familial AD
- Raises substantial ethical considerations, particularly around germline editing
APOE and risk modulation
- Research is exploring strategies to modify APOE expression or function, especially APOE ε4, to reduce risk and slow progression
Polygenic risk scores and personalized risk prediction
- May guide earlier surveillance and targeted preventive interventions, especially in high-risk populations
For future clinicians, literacy in genetics and genomics will be increasingly important in counseling patients and families about risk, screening, and potential enrollment in precision trials.
Treatment Innovations in Clinical Practice: From Lifestyle to Technology
While disease-modifying therapies attract most headlines, comprehensive, multidisciplinary care remains the cornerstone of Alzheimer’s management. This includes pharmacologic, lifestyle, psychosocial, and technological interventions that directly impact quality of life.
1. Lifestyle Interventions and Cognitive Health Promotion
Evidence from large studies (such as FINGER and related trials) suggests that multidomain lifestyle interventions can reduce cognitive decline risk:
Diet and Nutrition
- Mediterranean and MIND diets
- Emphasize fruits, vegetables (especially leafy greens), whole grains, legumes, fish, nuts, and olive oil
- Limit red meat, processed foods, and added sugars
- Associated with reduced risk of cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s Disease
Practical counseling points for clinicians:
- Encourage patients at risk to adopt a MIND-style diet early in midlife
- Collaborate with dietitians to tailor plans considering comorbidities (e.g., diabetes, CKD)
Physical Activity
Regular aerobic exercise (e.g., brisk walking 150+ minutes/week) and strength training improve:
- Cerebral blood flow
- Neurogenesis (particularly in the hippocampus)
- Vascular and metabolic health
Even in early dementia, supervised exercise programs can:
- Support function and mobility
- Improve mood and sleep
Cognitive and Social Engagement
- Cognitive stimulation: language learning, puzzles, musical training, complex hobbies, continuing education
- Social interaction: group activities, community centers, structured day programs
These activities are thought to build cognitive reserve, delaying the clinical expression of pathology.
2. Non-Pharmacological Therapies and Behavioral Management
Non-drug interventions are essential for managing behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD):
Cognitive training and rehabilitation
- Structured sessions focused on memory strategies, attention, and problem-solving
- Particularly helpful in MCI and early dementia
Occupational and environmental interventions
- Home safety assessments
- Simplified routines, clear cues, and visual reminders
- Reduction of sensory overload (noise, clutter)
Psychosocial interventions
- Validation therapy and reminiscence therapy
- Caregiver education to manage agitation, wandering, and sleep disturbances without reflexive reliance on antipsychotics
These approaches align with ethical principles of nonmaleficence and respect for dignity, particularly when pharmacologic options carry significant side effects.
3. Pharmacologic Symptomatic Treatments
Although not curative, symptomatic medications remain important:
Cholinesterase inhibitors (donepezil, rivastigmine, galantamine)
- Modest improvements in cognition and global functioning, primarily in mild to moderate AD
Memantine
- NMDA receptor antagonist used in moderate to severe AD
- May improve or stabilize cognition, behavior, and functional status
Judicious use of antidepressants, anxiolytics, or antipsychotics may be necessary, but only after non-pharmacologic options are exhausted and with close monitoring.
4. Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Digital Tools
Emerging technologies offer novel ways to stimulate cognition, support independence, and connect patients and families:
VR-based cognitive training
- Immersive environments for memory exercises, navigation tasks, and social interaction simulation
- Early studies suggest potential benefits in engagement and mood
AR tools
- Overlay prompts or reminders onto the real environment to assist with navigation and daily tasks
- May support independent function in early disease stages
Cognitive health apps and wearables
- Track cognition, activity, sleep, and behavior patterns
- Provide data to clinicians and caregivers, enabling earlier intervention
5. Telehealth and Remote Monitoring
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated adoption of telehealth, which has particularly strong relevance in Alzheimer’s care:
- Remote cognitive assessments and follow-ups, especially for patients with mobility or transportation barriers
- Video visits with caregivers to discuss care plans, safety concerns, and behavioral issues
- Remote monitoring devices to track wandering, falls, or medication adherence
For trainees, mastering telemedicine skills is now part of core clinical competence in managing chronic neurodegenerative disorders.
Living and Leading Ethically in the Era of Alzheimer’s Innovations
As a future physician, your role extends beyond prescribing medications. Alzheimer’s care is inherently interdisciplinary and ethically complex.

Supporting Patients, Caregivers, and Communities
Caregiver support
- Screen caregivers for depression, anxiety, and burnout
- Link families to support groups, respite care, and social work services
- Acknowledge cultural differences in caregiving roles and expectations
Education and destigmatization
- Provide clear explanations of diagnosis, prognosis, and available resources
- Address myths (e.g., “normal aging” vs. pathological decline)
- Encourage planning for the future (advance directives, financial and legal planning)
Advocacy and public health
- Participate in community education initiatives about cognitive health
- Support policies that improve access to diagnostic tools, long-term care, and research funding
Ethical and Professional Considerations for Trainees
Informed consent and capacity
- Assess decision-making capacity thoughtfully and document clearly
- Involve patients in choices as long as possible, respecting autonomy
Equity in access to care and research
- Recognize disparities in diagnosis and treatment among racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic groups
- Encourage diverse representation in clinical trials and ensure culturally sensitive care
Communicating uncertainty
- Be transparent about what is known, what remains unclear, and the realistic goals of current treatments
- Frame research advancements as sources of hope but avoid overpromising
Involvement in Alzheimer’s care offers rich opportunities for personal development, ethical reflection, and leadership in medical innovations.
FAQ: Common Questions About Alzheimer’s Disease, Research, and Treatment
Q1: How is Alzheimer’s Disease different from normal aging?
Normal aging may involve slower processing speed or occasional forgetfulness (e.g., misplacing keys). Alzheimer’s Disease causes progressive, functionally significant impairment—repeatedly forgetting important information, getting lost in familiar places, difficulty managing finances or medications, and noticeable changes in judgment and personality. These changes interfere with independence and are not a normal part of aging.
Q2: Who is eligible for the new monoclonal antibody treatments for Alzheimer’s?
Generally, these therapies are considered for patients who:
- Have Mild Cognitive Impairment due to Alzheimer’s or mild Alzheimer’s dementia
- Have confirmed Alzheimer’s pathology through biomarkers (e.g., amyloid PET or CSF)
- Do not have contraindications on MRI (such as extensive microhemorrhages)
- Are willing and able to undergo periodic infusions and serial MRIs to monitor for ARIA
Eligibility criteria are evolving and vary by region and regulatory approvals, so consultation with a memory disorders specialist is recommended.
Q3: Can lifestyle changes really reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s Disease?
Evidence suggests that addressing modifiable risk factors can significantly reduce the risk or delay onset of dementia. Interventions with the strongest support include:
- Managing blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol
- Regular physical activity and resistance training
- Adhering to a Mediterranean or MIND diet
- Staying mentally and socially active
- Treating hearing loss and sleep apnea
These strategies are not a guarantee against Alzheimer’s, but they contribute meaningfully to overall cognitive health and brain resilience.
Q4: Are blood tests for Alzheimer’s now available and reliable?
Blood-based biomarkers (such as plasma p-tau217 and others) are a major Research Advancement and are beginning to enter clinical use in some settings. They show strong correlation with CSF and PET measures and may eventually streamline screening and monitoring. However, availability, cost, and validation across diverse populations are still in progress. For now, they often complement—rather than replace—traditional diagnostic tools.
Q5: What can medical students and residents do now to contribute to progress in Alzheimer’s care?
- Seek exposure to memory clinics, neurology, geriatrics, and psychiatry rotations
- Learn to perform and interpret basic cognitive assessments (MMSE, MoCA)
- Get involved in clinical trials, translational research, or community outreach projects related to neurodegenerative disorders
- Develop skills in empathetic communication, shared decision-making, and telehealth
- Advocate for equitable access to cognitive health services in your institution and community
Engagement at the trainee level not only advances your own career but also contributes to the collective effort to improve outcomes for patients with Alzheimer’s Disease.
As Research Advancements and Treatment Innovations continue to accelerate, the field of Alzheimer’s Disease is shifting from resignation to realistic optimism. For the next generation of physicians, this is a defining area where clinical excellence, ethical practice, and scientific curiosity intersect to shape the future of cognitive health.



















