
The Ultimate Guide to Step 2 CS: What You Need to Know for Clinical Skills Success
Medical students and international medical graduates alike recognize how central the USMLE is to medical education and eventual licensure in the United States. Among its components, Step 2 Clinical Skills (CS) has been one of the most distinctive, because it evaluates how you perform where it matters most: with real (standardized) patients, in realistic clinical settings.
Even though the traditional Step 2 CS exam has been discontinued in its original format, many medical schools, clinical skills exams, and residency preparation programs still model their assessments and OSCEs (Objective Structured Clinical Examinations) after Step 2 CS standards. The skills tested—empathetic communication, focused physical examination, clinical reasoning, and accurate documentation—remain essential for USMLE-style Clinical Skills assessments, OSCEs, and residency interviews.
This enhanced guide walks through what Step 2 CS-style exams assess, how they are structured, and how to prepare strategically. It is designed to help you build strong clinical skills, perform confidently in any standardized patient exam, and demonstrate readiness for residency.
Understanding Step 2 CS and Clinical Skills Exams
What Was Step 2 CS—and Why Does It Still Matter?
Step 2 CS was one of the three original components of the USMLE, focusing specifically on clinical skills in a simulated patient care environment. While the exam itself has been phased out, its competencies are still embedded in:
- Medical school clinical skills courses
- OSCEs and clinical performance exams
- Institutional clinical skills assessments for progression or graduation
- Residency programs’ expectations for incoming interns
Step 2 CS-style exams are designed to assess whether you can:
- Take a focused, patient-centered history
- Perform an appropriate, respectful physical exam
- Develop a prioritized differential diagnosis
- Communicate clearly and empathetically
- Document your findings and reasoning in a structured note
These are the same competencies you’ll use daily in residency and throughout your career.
Key Domains Assessed in Clinical Skills Exams
Historically, Step 2 CS and current Step 2 CS–style OSCEs typically evaluate four major domains:
Communication and Interpersonal Skills
- Building rapport and trust
- Demonstrating empathy and respect
- Using understandable, non-technical language
- Addressing patient concerns and expectations
- Checking for understanding and inviting questions
History Taking and Clinical Reasoning
- Eliciting a focused and relevant history based on the chief complaint
- Asking both open- and closed-ended questions effectively
- Exploring symptom details (OLD CARTS, OPQRST, etc.)
- Considering red-flag symptoms and safety issues
- Generating a prioritized, reasonable differential diagnosis
Physical Examination Techniques
- Choosing the correct exam maneuvers for the presenting complaint
- Performing the exam systematically, efficiently, and respectfully
- Explaining what you are doing to the patient
- Maintaining appropriate draping and patient comfort
- Recognizing when a focused vs broader exam is needed
Documentation and Patient Note Writing
- Organizing information using a structured format (often SOAP)
- Clearly summarizing key subjective and objective findings
- Listing a prioritized differential diagnosis with supporting evidence
- Outlining an appropriate initial diagnostic and management plan
These domains mirror expectations in residency program evaluations and clinical performance reviews, which is why preparing thoughtfully for Step 2 CS–style exams is still a critical part of exam preparation and professional development.
Exam Format: What to Expect in Step 2 CS–Style Clinical Skills Assessments
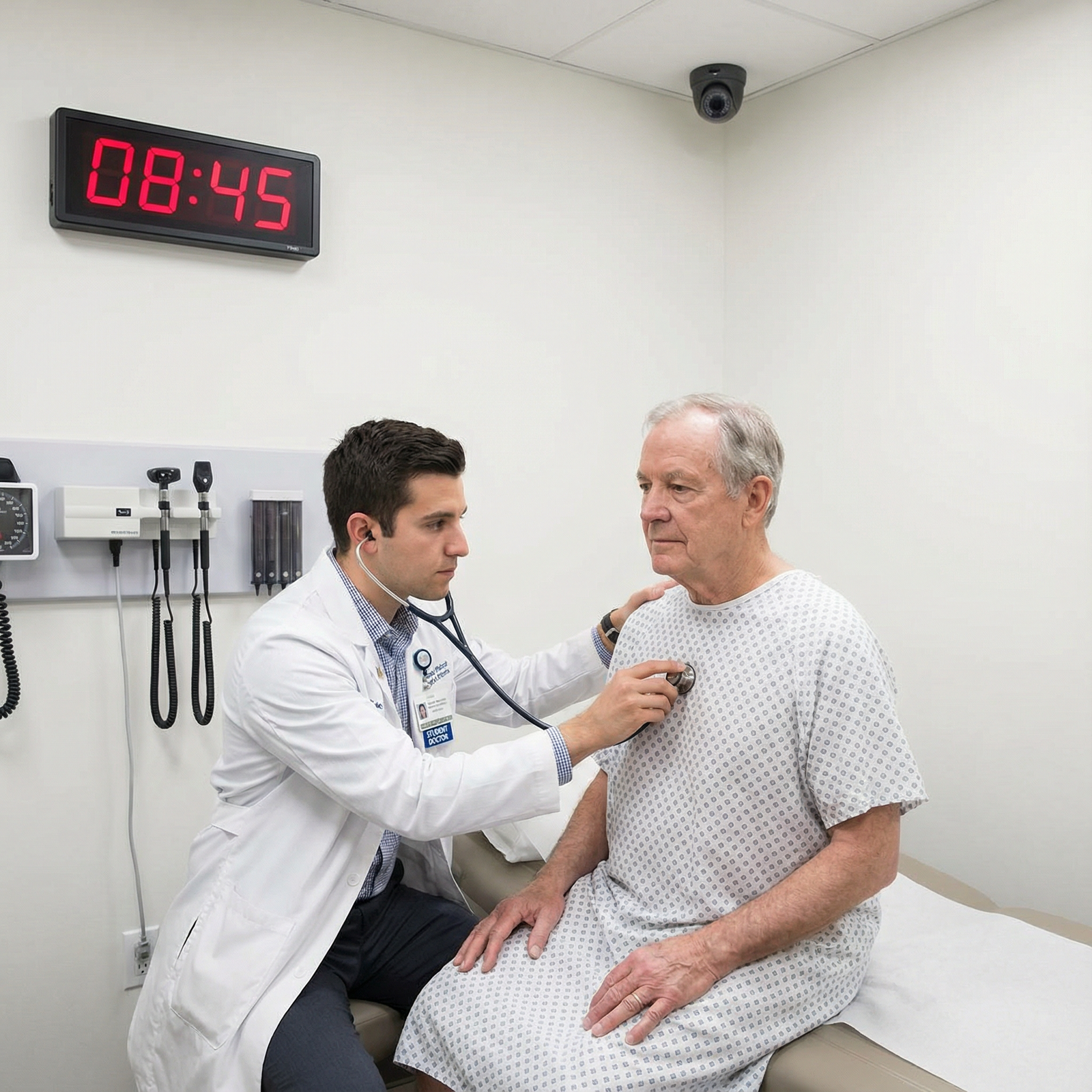
Overall Structure and Timing
Most Step 2 CS–style exams and OSCEs follow a similar template to the original exam:
- Total Exam Length: Approximately 7–8 hours, often split into morning and afternoon sessions
- Number of Cases: Typically 10–12 standardized patient encounters
- Time per Case:
- 10–15 minutes with the patient (history + physical exam)
- 5–10 minutes to write a patient note afterward
Between cases, you will usually have a brief interval to reset, move to the next room, and mentally shift to a new scenario.
Types of Clinical Scenarios You’ll Encounter
You can expect a broad range of patient presentations designed to reflect real-world ambulatory and emergency visits. Common categories include:
Acute Presentations
- Chest pain, shortness of breath, acute abdominal pain
- Headache, dizziness, syncope
- Trauma-related complaints (e.g., ankle injury, back pain)
Chronic Disease Management
- Diabetes follow-up and complications
- Hypertension, hyperlipidemia, coronary artery disease
- COPD, asthma, chronic kidney disease
Psychiatric and Behavioral Health
- Depression, anxiety, suicidal ideation
- Substance use disorders
- Somatic symptom presentations
Preventive Care and Counseling
- Smoking cessation
- Vaccination discussions
- Screening tests (e.g., colon, breast, cervical cancer)
Special Populations and Sensitive Topics
- Women’s health (e.g., abnormal bleeding, pregnancy concerns)
- Men’s health (e.g., erectile dysfunction, prostate symptoms)
- Sexual history, STI concerns, intimate partner violence
- Elderly patients with cognitive concerns or falls
The goal is not to “memorize cases” but to develop structured approaches that work across a wide variety of scenarios.
Breaks and Logistics
Typical Step 2 CS–style exams incorporate:
- 45 minutes to 1 hour of breaks across the day
- Short breaks between clusters of cases
- A longer mid-session break for lunch
Use breaks strategically for brief review (if allowed), hydration, nutrition, and mental reset. Long days test not just your knowledge, but your stamina and consistency.
Strategic Preparation for Step 2 CS–Style Clinical Skills Exams
Effective exam preparation is about practicing how you think and behave in the room, not just what you know. Treat this as both an exam preparation and professional development opportunity.
High-Yield Study Resources for Clinical Skills
Classic Step 2 CS Review Books
- First Aid for the USMLE Step 2 CS
- USMLE Step 2 CS: The Complete Study Guide
These books provide case templates, sample patient notes, and checklists for common presentations. Even though the original exam has changed, these remain excellent references for OSCE-style preparation.
Online Case Banks and Videos
- UWorld Step 2 CK “clinical skills” style questions can strengthen reasoning and note-writing
- Kaplan, AMBOSS, and other platforms often include clinical scenarios that mirror Step 2 CS complexity
- Video-based OSCE demonstrations from medical schools (e.g., on YouTube) can help you visualize strong encounters
Institutional Clinical Skills Courses
- Most medical schools provide clinical skills sessions with standardized patients
- Take these seriously—arrive prepared, ask for feedback, and apply that feedback deliberately
Faculty and Resident Mentors
- Ask for observation and feedback in clinics and wards
- Request targeted coaching on patient communication, presenting your differential, and structuring assessments/plans
Practice Partners and Peer Groups
- Small groups (2–4 students) can recreate exam-style encounters:
- One plays the patient
- One the clinician
- Others observe and use checklists to give feedback
- Small groups (2–4 students) can recreate exam-style encounters:
Building Core Skills: What to Focus On
1. Communication Techniques and Bedside Manner
Strong communication is central to every clinical skills exam—and to real-world practice.
Concrete strategies:
Start every encounter with:
- Knock, enter, hand hygiene
- “Hello, Mr./Ms. [Name], my name is [Your Name]. I’m a medical student working with the team today.”
- Confirm patient’s name and how they prefer to be addressed
Use structured interviewing:
- Begin with open-ended questions: “What brings you in today?”
- Then narrow with focused questions guided by the chief complaint
- Ask about impact on work, family, daily functioning
Demonstrate empathy explicitly:
- “I’m sorry you’re going through this; it sounds really difficult.”
- “I can see this has been worrying you.”
Check understanding and invite questions:
- “Does that explanation make sense?”
- “What questions or concerns do you have?”
Avoid jargon: Translate medical language into simple, clear terms.
Practicing these scripts repeatedly will make them feel natural and automatic on exam day.
2. Physical Exam Skills Under Time Pressure
Time-limited exams demand focused examinations tailored to the problem.
Examples:
Chest pain case:
- Vital signs review (if provided)
- General inspection
- Cardiac exam: inspection, palpation, auscultation
- Pulmonary exam
- Peripheral vascular: pulses, edema, calf tenderness (if appropriate)
Abdominal pain:
- Inspect, auscultate, percuss, palpate
- Assess for rebound/guarding
- Check CVA tenderness
Joint pain:
- Inspect for swelling, redness, deformity
- Palpate joint and surrounding structures
- Assess range of motion (active then passive)
Always:
- Explain each step to the patient
- Maintain appropriate draping and respect for privacy
- Stop if the patient experiences significant pain
Practice complete exam sequences frequently until they are smooth and efficient.
3. Clinical Reasoning and Differential Diagnosis
Examiners look closely at how you think. Your differential should be:
- Prioritized (most likely and dangerous diagnoses first)
- Supported by specific history and exam findings
- Reasonable in breadth (typically 3–5 diagnoses)
For example, in a 55-year-old smoker with chronic cough and weight loss:
- #1: Lung cancer – supported by age, smoking, weight loss, chronic cough
- #2: COPD exacerbation – supported by chronic symptoms in a smoker
- #3: Tuberculosis – supported by chronic cough and weight loss, depending on exposure risk
- #4: GERD with chronic laryngitis – if symptoms include heartburn, nocturnal cough
You will also be judged on whether your initial workup and plan match your differential.
4. Patient Note and Documentation
Most clinical skills exams require a documentation format similar to a SOAP note:
- Subjective (S): Chief complaint, HPI, ROS, relevant PMH/PSH, meds, allergies, social and family history
- Objective (O): Vital signs and key physical exam findings
- Assessment (A): Brief summary statement + prioritized differential diagnoses with supporting evidence
- Plan (P): Initial diagnostic tests and management steps for each key diagnosis
Practice writing patient notes within strict time limits (5–10 minutes), aiming for:
- Clarity and organization
- Relevance—avoid padding notes with extraneous information
- Direct linkage between your history/exam and your differential
Practical Strategies and Test-Day Essentials
Clinical skills exams reward not just knowledge, but preparation, organization, and professionalism.
Test-Day Preparation: Set Yourself Up for Success
Dress Professionally
- Clean, pressed professional attire
- White coat if required by exam policies
- Closed-toe shoes, minimal jewelry, neat appearance
Bring Required Documents
- Valid, acceptable ID according to exam or institution guidelines
- Exam confirmation or scheduling permit if applicable
Manage Nutrition and Energy
- Eat a balanced meal before the exam; avoid heavy, greasy foods
- Bring snacks and water for breaks (if permitted)
- Consider caffeine habits—don’t substantially change your usual intake on exam day
Arrive Early
- Aim to arrive 30–45 minutes before check-in
- Use extra time to calm nerves, review general frameworks (not detailed notes), and get oriented
Performance Tips During the Exam
Use a Consistent Encounter Framework
- Knock, hand hygiene, introduce yourself
- Confirm patient’s identity and chief complaint
- Open-ended question → focused history → relevant ROS
- Targeted physical exam
- Brief summary and explanation of your differential
- Address questions, finalize plan, and close the encounter
Time Management Inside Each Room
- Allocate roughly:
- 7–9 minutes for history
- 3–5 minutes for physical exam
- 1–2 minutes for counseling and closure
- If you’re running behind, prioritize:
- Key history red flags
- The most critical physical maneuvers
- A clear, empathetic closing
- Allocate roughly:
Maintain Composure and Adaptability
- Expect at least one challenging or emotionally charged case
- If you feel one encounter went poorly, consciously reset before the next:
- Deep breath
- Mentally review your structured approach
- Focus only on the upcoming patient
Always Close the Encounter Professionally
- Summarize what you have learned: “From what you’ve told me and what I found on the exam…”
- Present a brief, understandable explanation of your thinking
- Outline next steps (“tests,” “imaging,” “specialist referral,” etc.)
- Ask: “What questions or concerns do you have?”
- Thank the patient for their time and trust
Respect Confidentiality and Professional Boundaries
- Avoid judgmental language
- Be especially sensitive during sexual, psychiatric, or substance use histories
- Emphasize confidentiality within the standard exceptions (e.g., safety concerns) when appropriate
Scoring, Feedback, and Continuous Improvement

How Clinical Skills Exams Are Scored
While each institution or exam center may have unique details, scoring generally aligns with three broad areas:
Integrated Clinical Encounter (ICE)
- Quality of history taken
- Appropriateness and completeness of physical exam
- Accuracy and organization of documentation
Communication and Interpersonal Skills (CIS)
- Empathy, respect, and professionalism
- Clarity of explanations and instructions
- Ability to build rapport and manage patient emotions
Spoken English Proficiency (SEP) (when applicable)
- Clarity of speech and pronunciation
- Comprehensibility to patients and examiners
- Appropriate vocabulary and grammar
Performance is often judged on a global pass/fail basis, but feedback typically highlights specific strengths and weaknesses in each domain.
Interpreting Results and Using Feedback
When you receive your results:
If You Pass:
- Review any available feedback to identify minor weaknesses
- Carry those lessons into clinical rotations and residency preparation
If You Do Not Pass (or Perform Below Expectations on an OSCE):
- Resist the urge to focus solely on the disappointment; instead:
- Analyze which domains were weakest: communication, exam skills, documentation, or reasoning
- Ask for detailed feedback from faculty or exam review committees
- Consider additional practice sessions with standardized patients or faculty observers
- Create a concrete improvement plan:
- Specific number of mock encounters per week
- Focused review of patient note writing
- Targeted practice for spoken English if needed
- Resist the urge to focus solely on the disappointment; instead:
Remember: improving clinical skills is a continuous process, not just an exam requirement.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Step 2 CS–Style Clinical Skills Exams
Q1: When is the best time during medical school to take a Step 2 CS–style exam?
Most students perform best after completing several core clinical clerkships (e.g., internal medicine, family medicine, surgery, pediatrics, OB/GYN, psychiatry). By then, you have enough clinical exposure to handle common presentations and communicate comfortably with patients. If your school has flexibility, taking the exam late in the third year or early in the fourth year aligns well with residency exam preparation and application timelines.
Q2: How difficult are Step 2 CS–style clinical skills exams compared to written exams like Step 2 CK?
They are challenging in a different way. Rather than test recall of facts, clinical skills exams assess your ability to apply knowledge in real-time, interact with patients, and think on your feet. Many students underestimate the difficulty because it “feels like clinical work,” but time pressure, standardized expectations, and structured scoring can make performance more demanding than a typical clinic day. Appropriate, deliberate practice usually leads to success.
Q3: Can I bring personal notes or reference materials into the exam?
No. Just like the original USMLE Step 2 CS, clinical skills exams typically do not allow external notes, textbooks, or electronic resources during patient encounters or note-writing. You must rely on your internalized frameworks for history taking, physical exams, differentials, and documentation. This is why repeated simulation and practice are essential parts of effective exam preparation.
Q4: What should I focus on if English is not my first language?
If spoken English proficiency is a concern:
- Practice common patient interview phrases until fluent and automatic
- Record yourself conducting mock interviews and listen for clarity, speed, and pronunciation
- Ask native or fluent English-speaking peers or mentors for feedback
- Avoid overly complex vocabulary—clarity is more important than sounding “fancy”
- Slow slightly when explaining diagnoses and plans; pause to check understanding
Strong empathy, clear structure, and visible effort to ensure patient understanding can significantly improve your communication scores, even with an accent.
Q5: How do results from clinical skills exams impact residency applications and my medical education progression?
For many schools and institutions, passing a clinical skills exam is a graduation requirement and a marker of readiness for residency. While specific scoring details may or may not appear on your residency application, program directors care deeply about:
- Communication and professionalism
- Reliability, organization, and clinical reasoning
- Evidence that you can handle patient encounters independently at an intern level
Strong performance—and especially documented improvements over time—can also give your mentors concrete examples of your growth to highlight in letters of recommendation.
Mastering Step 2 CS–style clinical skills exams is more than an academic hurdle; it is a critical step in your development as a safe, effective, and compassionate physician. By understanding the exam format, investing in targeted exam preparation, and using every patient encounter—real or simulated—as an opportunity to improve, you’ll build the confidence and competence that will serve you throughout residency and beyond.


















